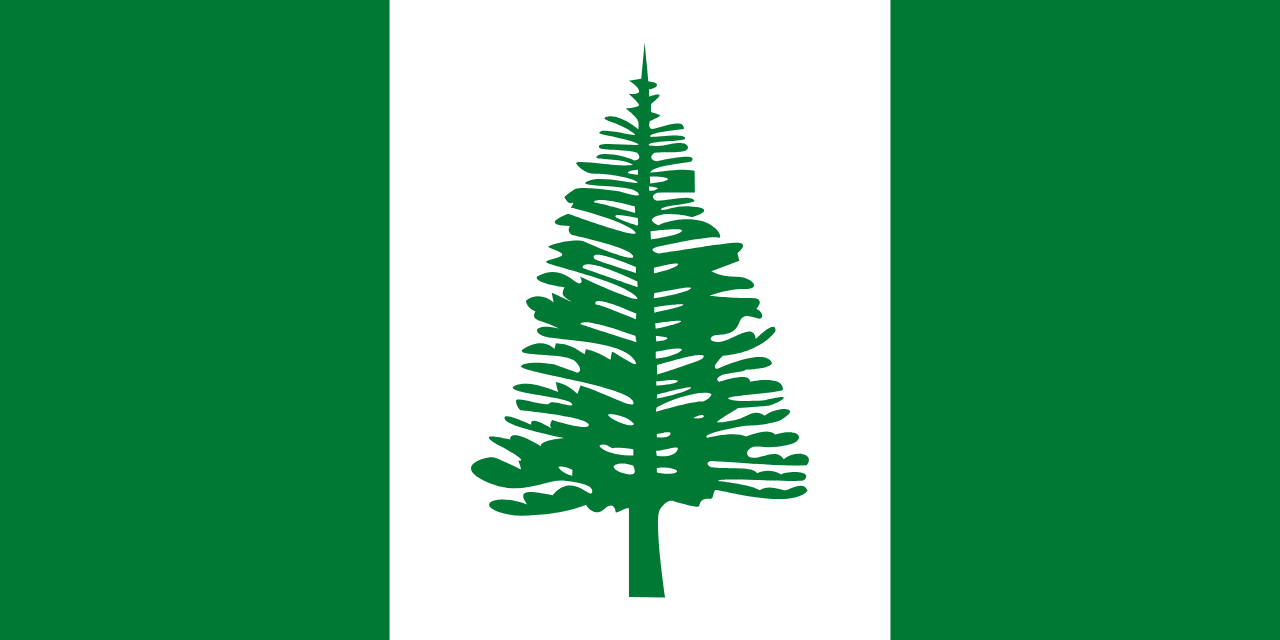
Norfolk Island Flag Meaning
Vertical green stripe and white field featuring the iconic Norfolk Pine, symbol of the island's unique heritage.
- Continent
- Oceania
- Adopted
- 1979
- Ratio
- 1:2
- Colors
- green, white
Symbolism
Green Vertical Stripe: Represents the rich vegetation and lush landscape of Norfolk Island, particularly its famous pines and other endemic flora.
White Field: Symbolizes peace, the island's isolation in the vast Pacific Ocean, and the hope for a peaceful future for its people.
Norfolk Pine: The central emblem represents the Norfolk Island Pine (Araucaria heterophylla), an endemic species that has become the island's most recognizable symbol.
Tree's Central Position: The pine's placement in the center reflects its importance to the island's identity and its role as a landmark visible from great distances at sea.
History
- 1774: Captain James Cook discovered and named Norfolk Island, noting the abundance of flax plants and tall pine trees suitable for ship masts.
- 1788-1814, 1825-1855: Norfolk Island served as a British penal colony, with the Norfolk Pine becoming a symbol of both isolation and endurance for convicts and guards.
- 1856: Pitcairn Islanders, descendants of HMS Bounty mutineers, settled on Norfolk Island, bringing their unique culture and heritage.
- 1979: The current flag was officially adopted when Norfolk Island gained limited self-government as an Australian external territory.
- 1979-present: The flag has remained unchanged, representing the island's stable identity despite various administrative changes with Australia.
Trivia
- Norfolk Island is one of the few places in the world where the national tree (Norfolk Pine) is featured prominently on the flag.
- The Norfolk Pine can grow up to 65 meters tall and live for over 200 years, making it a fitting symbol of endurance.
- Norfolk Island has its own language called Norfuk, a creole mixture of English and Tahitian brought by the Pitcairn settlers.
- The island has a population of only about 1,750 people, making it one of the least populous territories with its own flag.
- Norfolk Pines were historically so valuable for ship masts that they were protected by British naval law in the 18th century.
- The flag is flown alongside the Australian flag, as Norfolk Island is an Australian external territory.
- Norfolk Island was uninhabited when Europeans arrived, but archaeological evidence suggests earlier Polynesian settlement.
- The island operates on its own time zone (Norfolk Island Time), which is 30 minutes ahead of Australian Eastern Standard Time.
- Norfolk Island has its own postal system and issues its own stamps, often featuring the Norfolk Pine design.
Related Countries
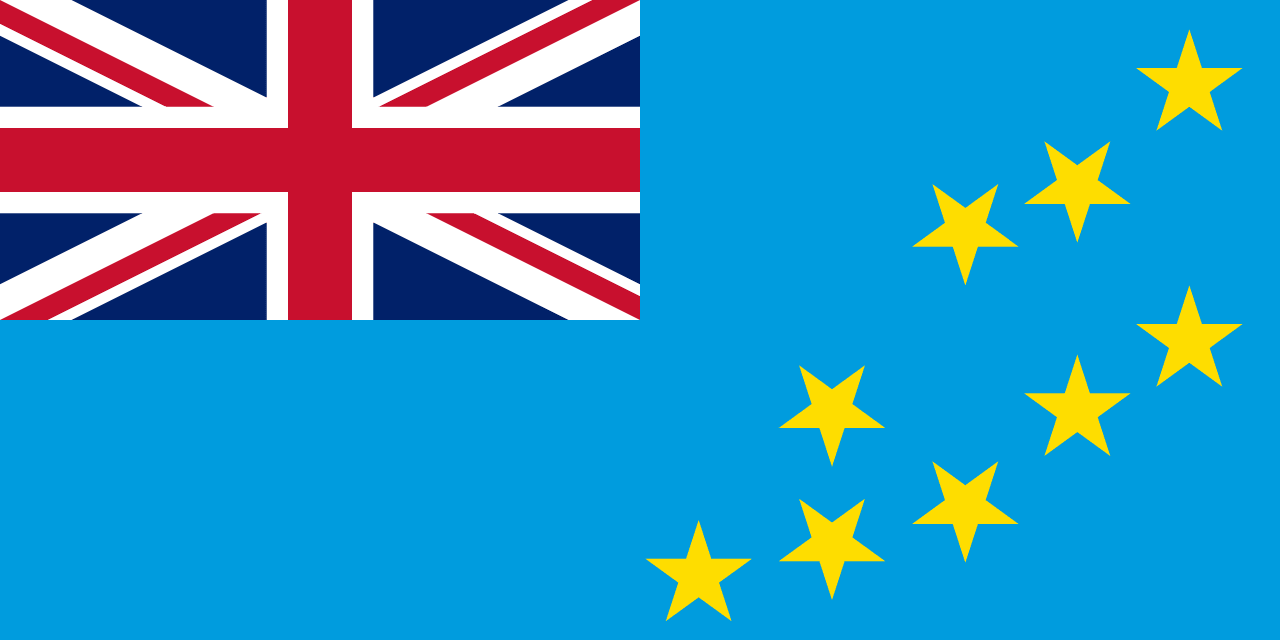
Tuvalu
Oceania
A light blue field with the Union Jack in the canton and nine yellow stars representing the nine atolls of Tuvalu, symbolizing the Pacific Ocean that surrounds the islands, the historical connection to Britain, and the geographical arrangement of the island nation in the central Pacific.
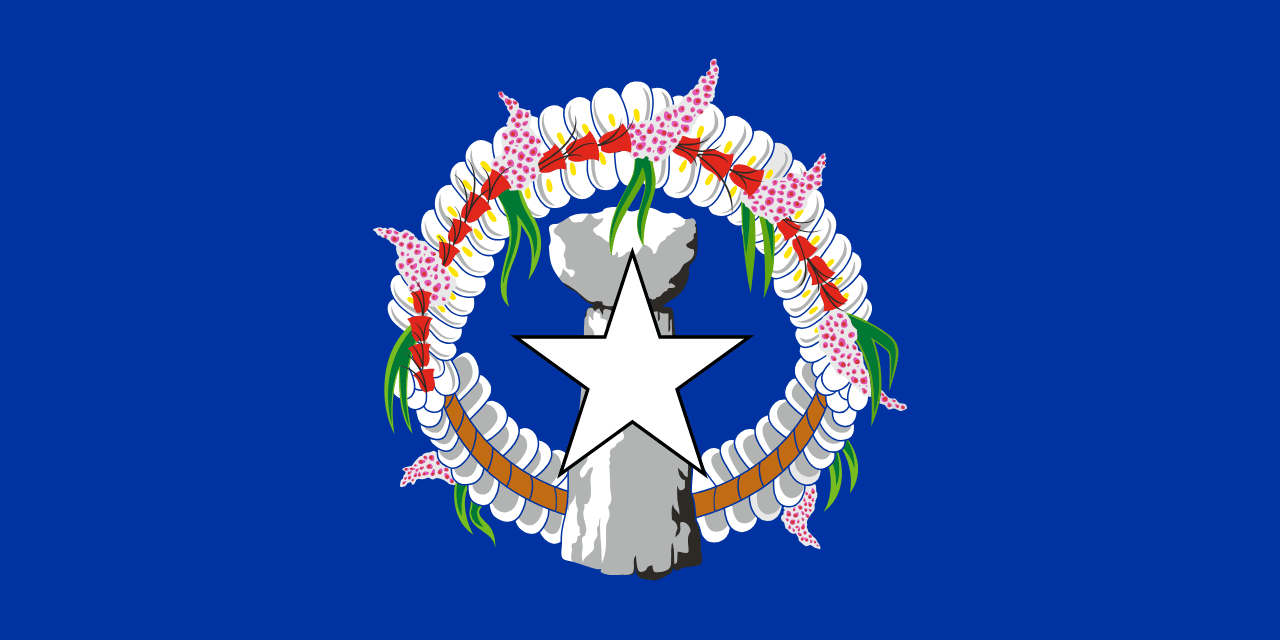
Northern Mariana Islands
Oceania
A blue field with a white star and gray latte stone behind it, surrounded by a decorative wreath. The flag represents the islands’ indigenous culture, U.S. affiliation, and Pacific identity.
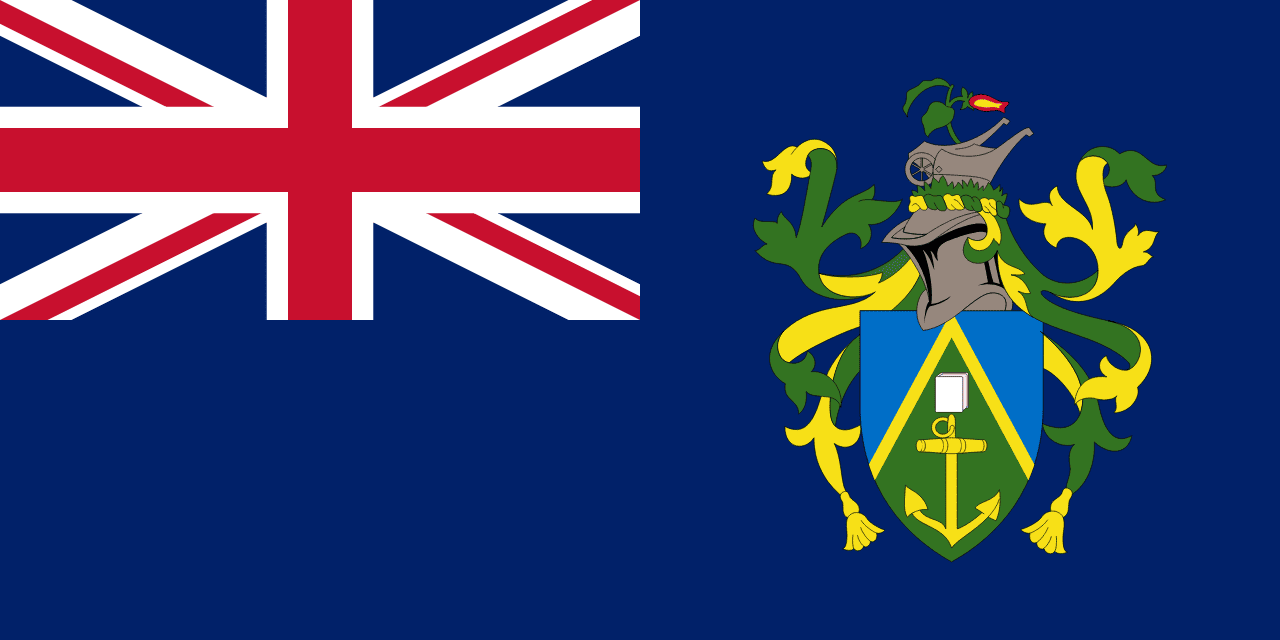
Pitcairn Islands
Oceania
Blue ensign with Union Jack and coat of arms featuring the Bible, anchor, and wheelbarrow symbolizing faith, maritime heritage, and agriculture.
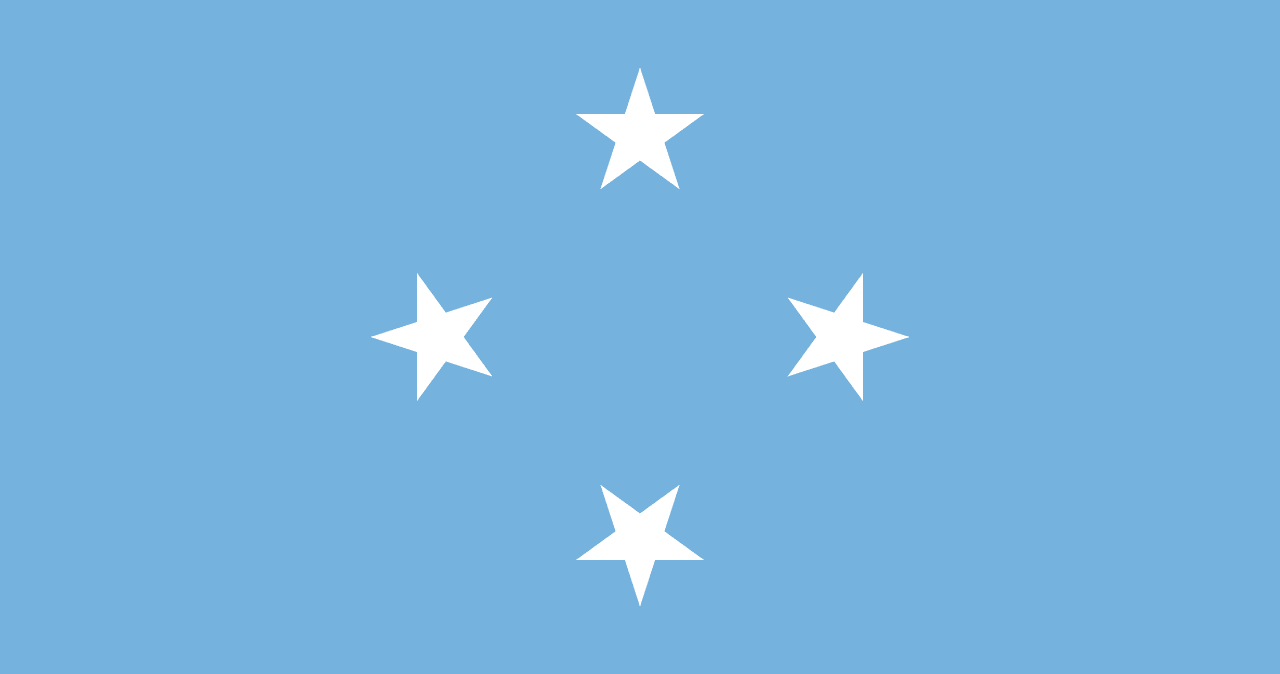
Micronesia
Oceania
Four white five-pointed stars arranged in a diamond pattern on a light blue field, representing the four states of the Federated States of Micronesia surrounded by the Pacific Ocean.
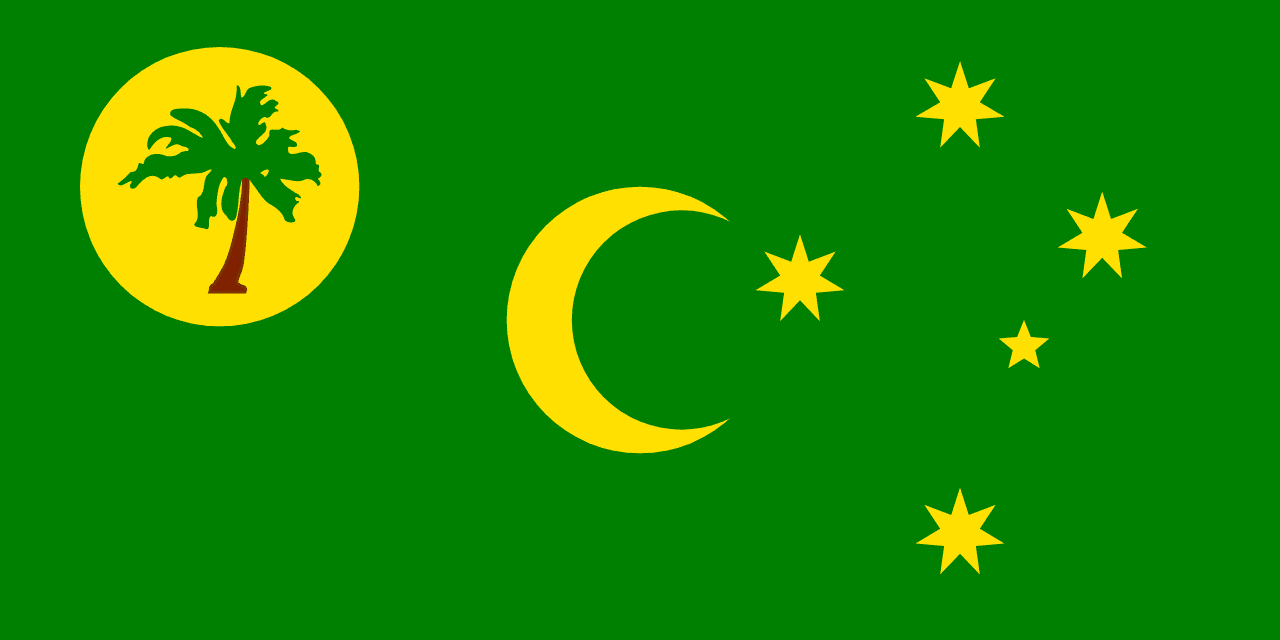
Cocos Islands
Oceania
Green field with golden disc, crescent moon, palm tree, and Southern Cross representing the Malay Muslim community, tropical environment, and Australian connection.
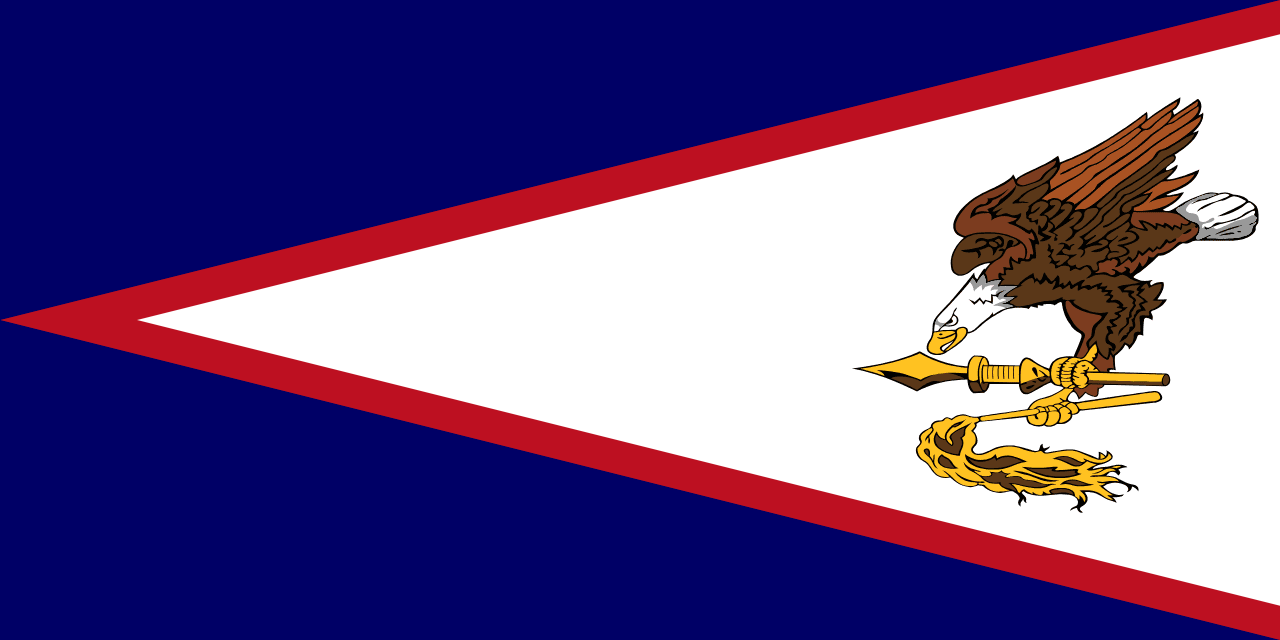
American Samoa
Oceania
Red, white, and blue field featuring a bald eagle holding traditional Samoan symbols, representing the blend of American and Polynesian cultures.