Tanzania Flag Meaning
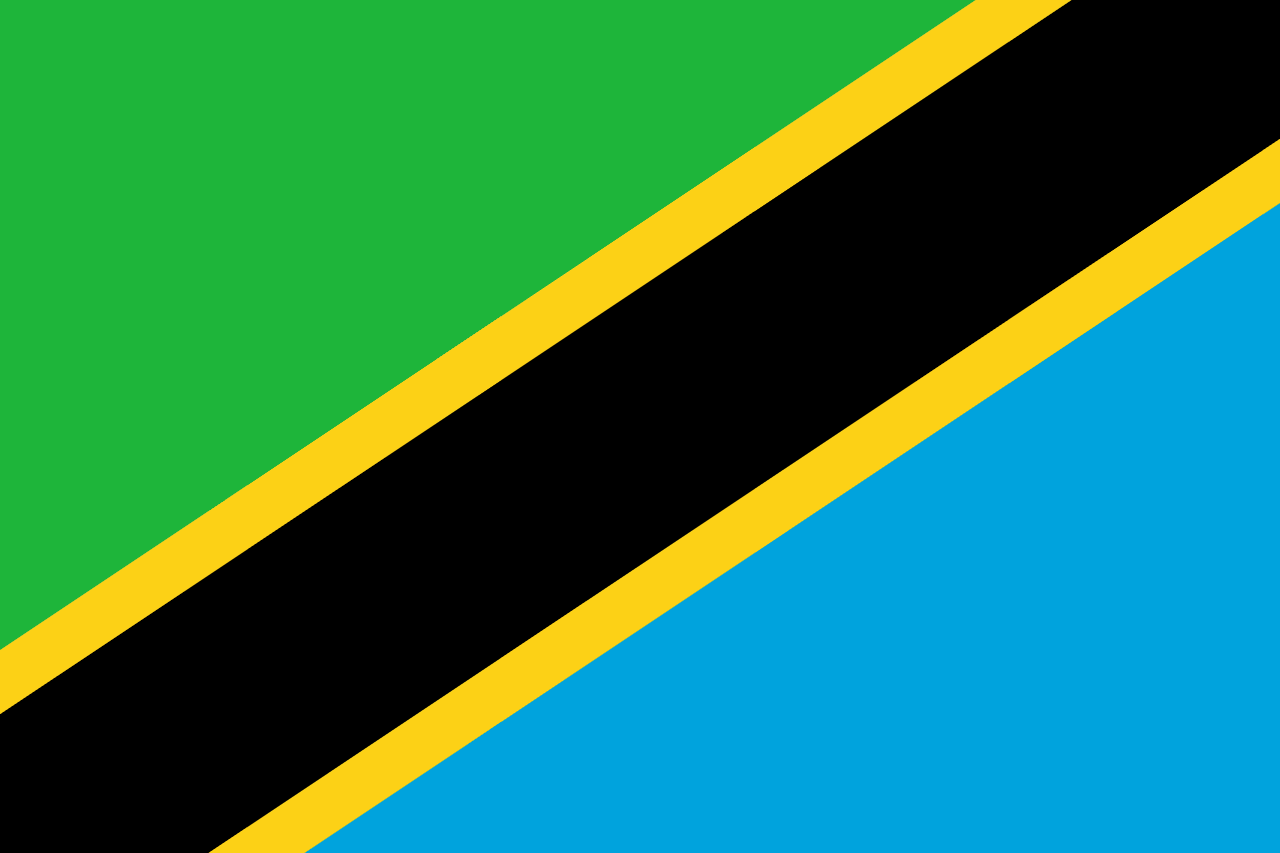
A green triangle in the upper hoist, a blue triangle in the lower fly, separated by a diagonal black stripe bordered by yellow stripes, representing the country's agriculture and forests, mineral wealth, the African people, and the Indian Ocean, symbolizing the union of Tanganyika and Zanzibar.
- Continent
- Africa
- Adopted
- 1964
- Ratio
- 2:3
- Colors
- green, yellow, black, blue
- Designer
- Unknown
Symbolism
Green Triangle: Represents the rich agricultural land and natural vegetation of Tanzania, symbolizing the forests, farmland, and environmental wealth that sustain the predominantly rural population.
Blue Triangle: Represents the Indian Ocean, lakes, and rivers that provide water resources and fishing opportunities, symbolizing the maritime heritage and the importance of water for life and commerce.
Black Diagonal Stripe: Represents the African people and their heritage, symbolizing the unity of the diverse ethnic groups that make up Tanzania and their shared identity as Africans.
Yellow Borders: Represent the mineral wealth of Tanzania, including gold, diamonds, and other precious resources, symbolizing the economic potential and natural riches of the country.
Diagonal Design: The diagonal division represents the union of Tanganyika (mainland) and Zanzibar (islands), symbolizing the political federation that created modern Tanzania in 1964.
History
- Pre-Colonial Era: Various Bantu-speaking peoples migrated into the region over centuries, while Arab and Persian traders established settlements along the coast, creating Swahili culture and trade networks.
- 1498-1698: Portuguese control of the East African coast was gradually replaced by Omani Arab rule, particularly in Zanzibar, which became a major center of the Indian Ocean slave and spice trade.
- 1840s-1880s: Zanzibar under Sultan Seyyid Said became the dominant power on the East African coast, controlling trade routes and establishing clove plantations worked by enslaved labor.
- 1885-1918: German East Africa was established on the mainland (Tanganyika), introducing colonial administration, forced labor, and cash crop cultivation while Zanzibar remained under British influence.
- 1919-1961: Britain administered Tanganyika as a League of Nations mandate and later UN trusteeship, gradually introducing limited self-government and education while maintaining colonial control.
- December 9, 1961: Tanganyika gained independence under Julius Nyerere's TANU party, becoming a republic in 1962 and beginning the process of African socialist development.
- December 10, 1963: Zanzibar gained independence from Britain, but a revolution in January 1964 overthrew the Arab government and established a socialist republic.
- April 26, 1964: Tanganyika and Zanzibar united to form the United Republic of Tanzania, adopting the current flag and creating one of Africa's largest countries.
- 1967-1985: Nyerere implemented 'Ujamaa' (African socialism), emphasizing self-reliance, village collectivization, and non-alignment, though economic results were mixed.
- 1985-1995: Ali Hassan Mwinyi succeeded Nyerere and began economic liberalization, moving away from socialist policies toward market-oriented reforms and multi-party democracy.
- 1995-Present: Democratic governance has continued with regular elections, though recent years have seen concerns about authoritarian tendencies and restrictions on civil society and media.
Trivia
- Tanzania is home to Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa's highest peak at 5,895 meters, and the Serengeti National Park, famous for the annual wildebeest migration.
- The flag represents Africa's largest country by area (947,300 sq km) and is home to over 120 different ethnic groups, yet has maintained remarkable peace and stability.
- Swahili (Kiswahili) is the national language and serves as a unifying factor across ethnic groups, making Tanzania one of the few African countries with a truly national language.
- Tanzania is the birthplace of humanity, with some of the oldest hominid fossils found at Olduvai Gorge, including remains that are over 3 million years old.
- The country has significant mineral wealth including gold, diamonds, tanzanite (found nowhere else in the world), and natural gas deposits off the coast.
- Zanzibar, the semi-autonomous archipelago, is known as the 'Spice Island' for its historic role in the clove, nutmeg, and cinnamon trade.
- Traditional music includes taarab from Zanzibar (influenced by Arab, Indian, and African styles) and ngoma drumming found throughout the mainland.
- The flag flies over a country where about 61% of the population is Christian, 35% Muslim (mostly on the coast and Zanzibar), with traditional religions also practiced.
- Tanzania has over 20 national parks and game reserves, protecting some of Africa's largest wildlife populations including elephants, lions, and rhinoceros.
- The economy is primarily agricultural, with most people engaged in subsistence farming, though coffee, tea, cotton, and cashews are important export crops.
- Dar es Salaam is the largest city and former capital, while Dodoma became the official capital in 1996, though government functions remain divided between both cities.
- Traditional foods include ugali (maize porridge), nyama choma (grilled meat), and various stews with beans, vegetables, and coconut-based coastal dishes.
- Tanzania pioneered African socialism under Julius Nyerere, who emphasized education, self-reliance, and pan-African solidarity, earning him the title 'Mwalimu' (teacher).
- The country faces development challenges including poverty, limited infrastructure, access to clean water and electricity, and pressure on natural resources from population growth.
- Despite economic difficulties, Tanzania has maintained political stability, peaceful elections, and ethnic harmony, making it a model for other African countries.
Related Countries
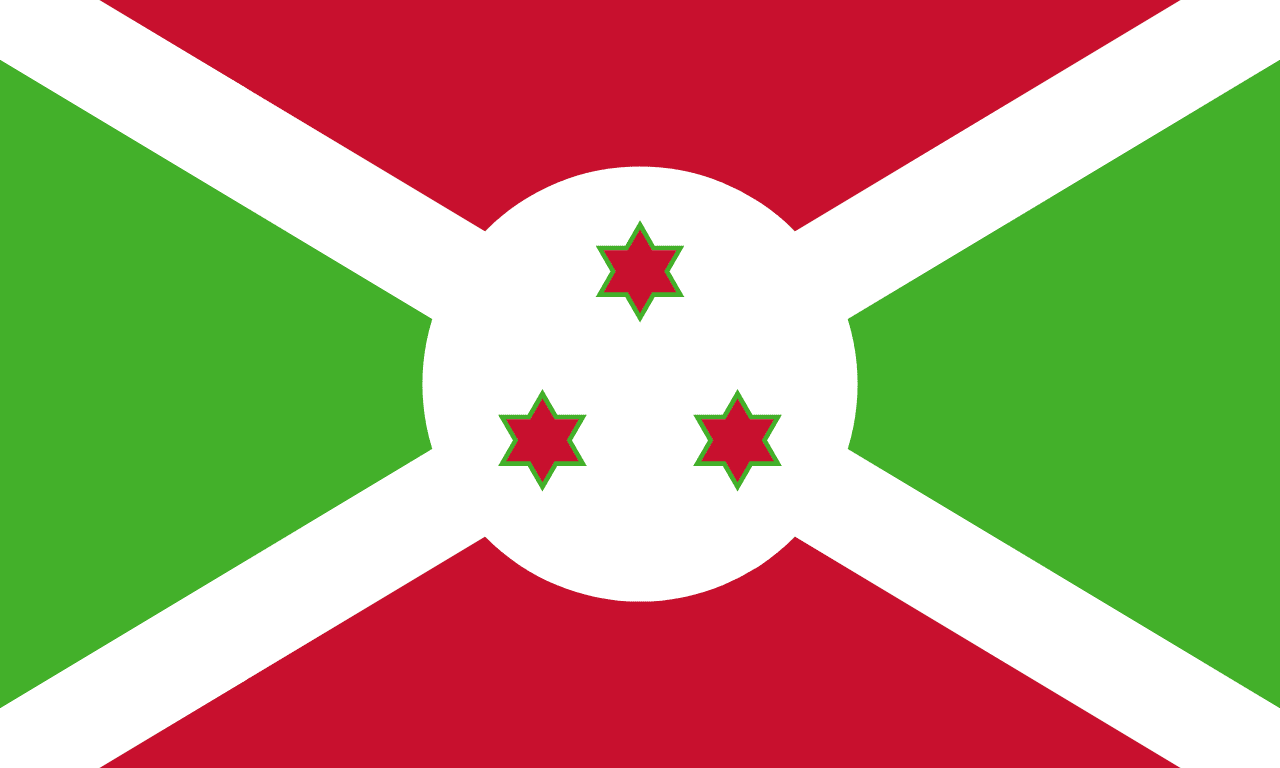
Burundi
Africa
A white diagonal cross dividing the flag into alternating red and green triangles, with three red stars outlined in green in the center circle, representing unity, work, progress, and the three ethnic groups of Burundi.
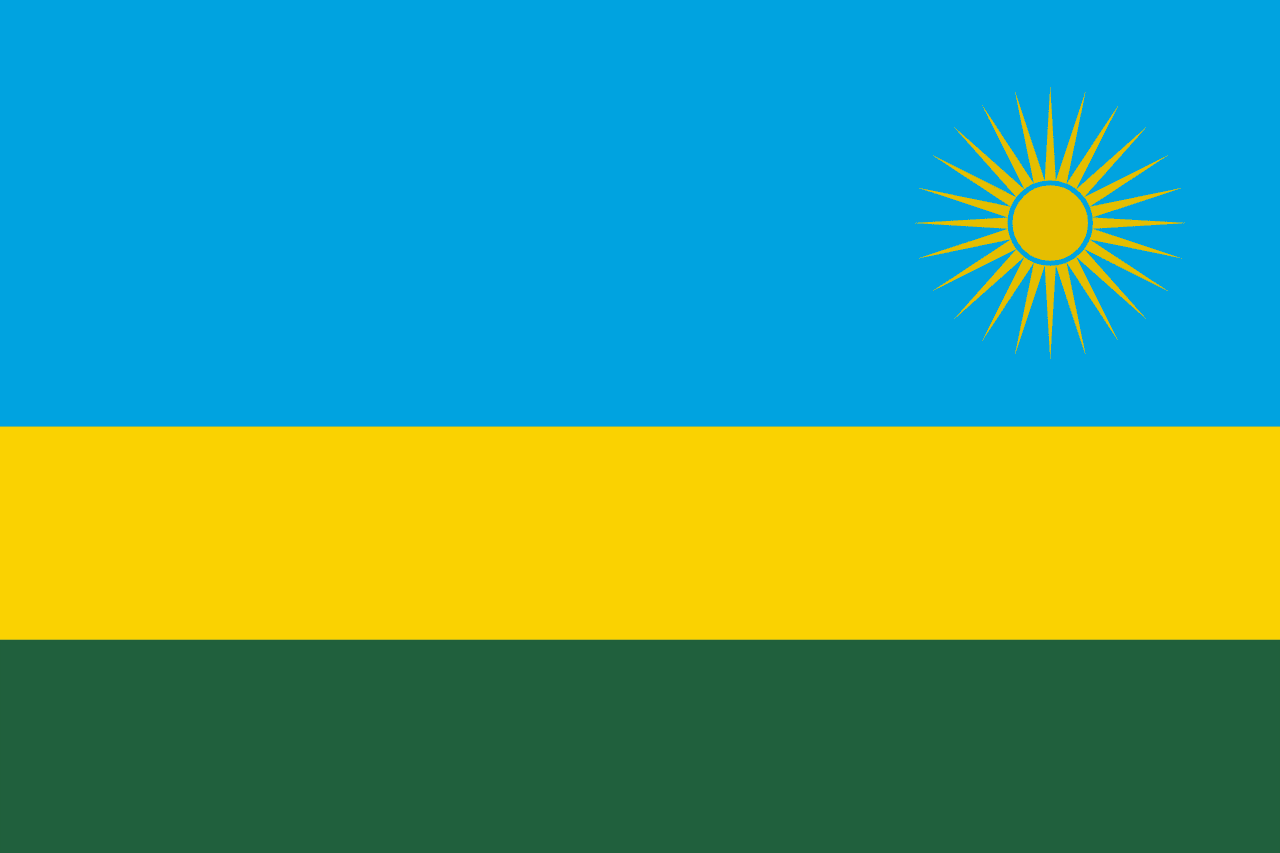

Rwanda
Africa
A tricolor of blue, yellow, and green bands with a golden sun in the upper fly corner. Adopted in 2001, the flag symbolizes unity, hope, and a new era of peace following the 1994 genocide.
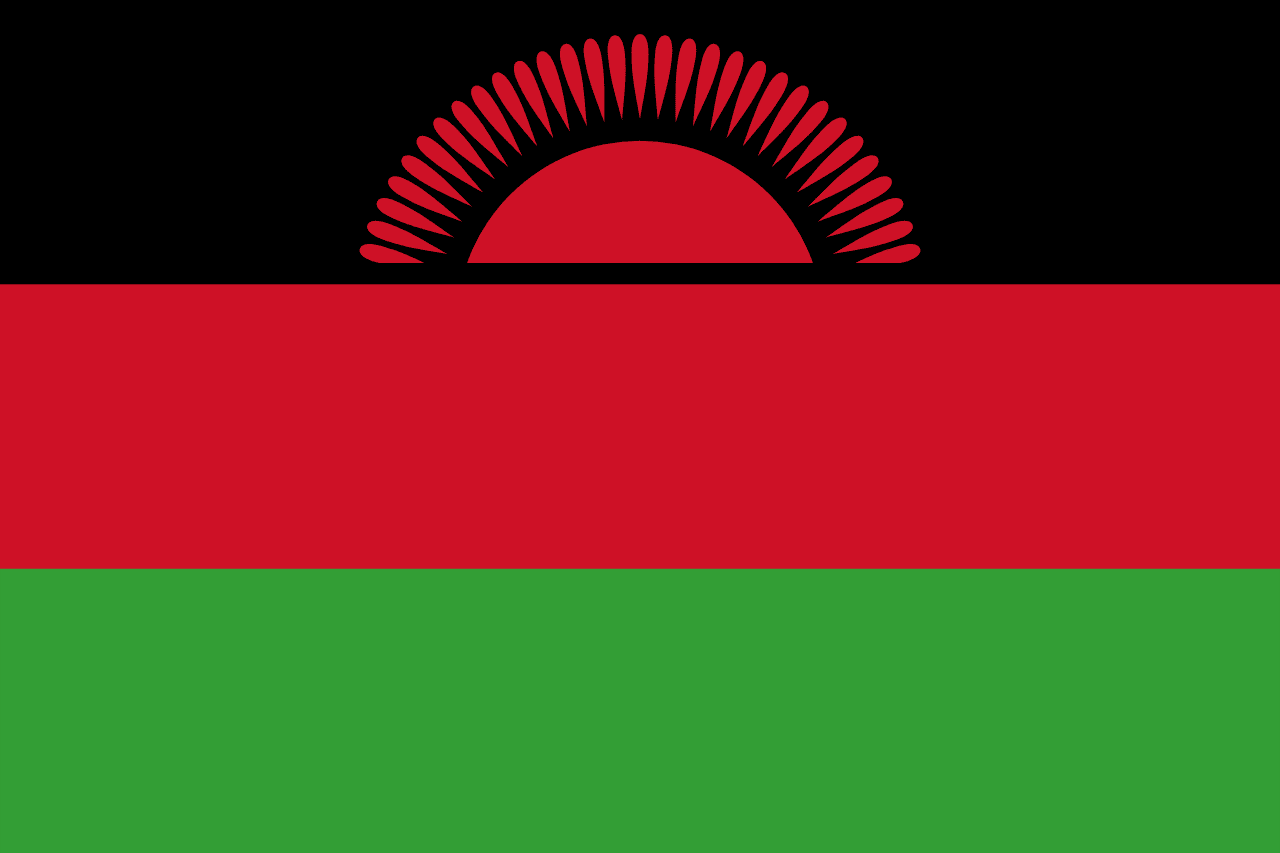

Malawi
Africa
Three horizontal stripes of black, red, and green with a red rising sun in the upper left corner, representing the African people, the blood of freedom fighters, the land's fertility, and the dawn of freedom and hope.
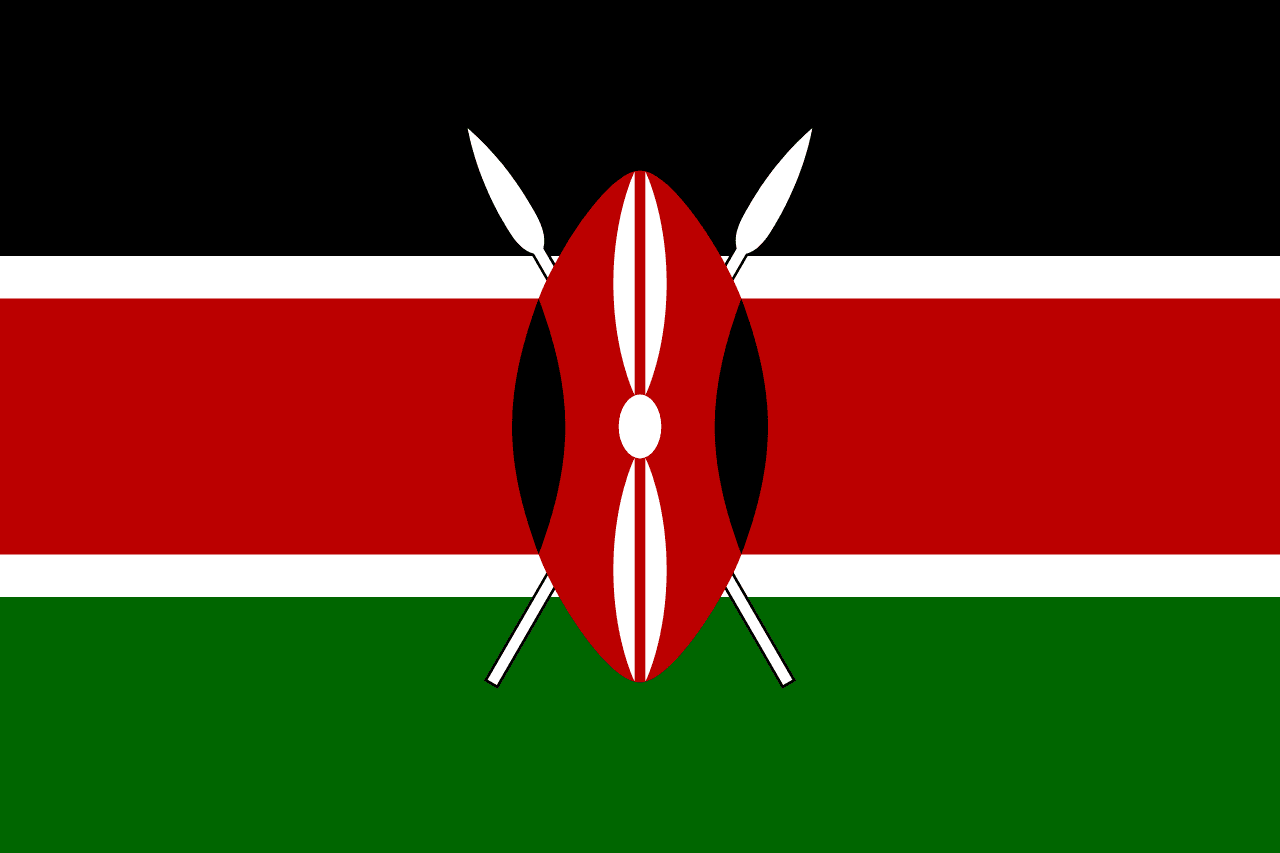
Kenya
Africa
Three horizontal stripes of black, red, and green separated by narrow white stripes, with a traditional Maasai shield and two crossed spears centered on the flag, representing Kenya's struggle for independence and the defense of freedom.

Uganda
Africa
Six horizontal stripes alternating black, yellow, and red (repeated twice) with a white circle containing the grey crowned crane in the center, representing the African people, sunshine and prosperity, brotherhood and unity, and the national bird that symbolizes Uganda's forward movement.
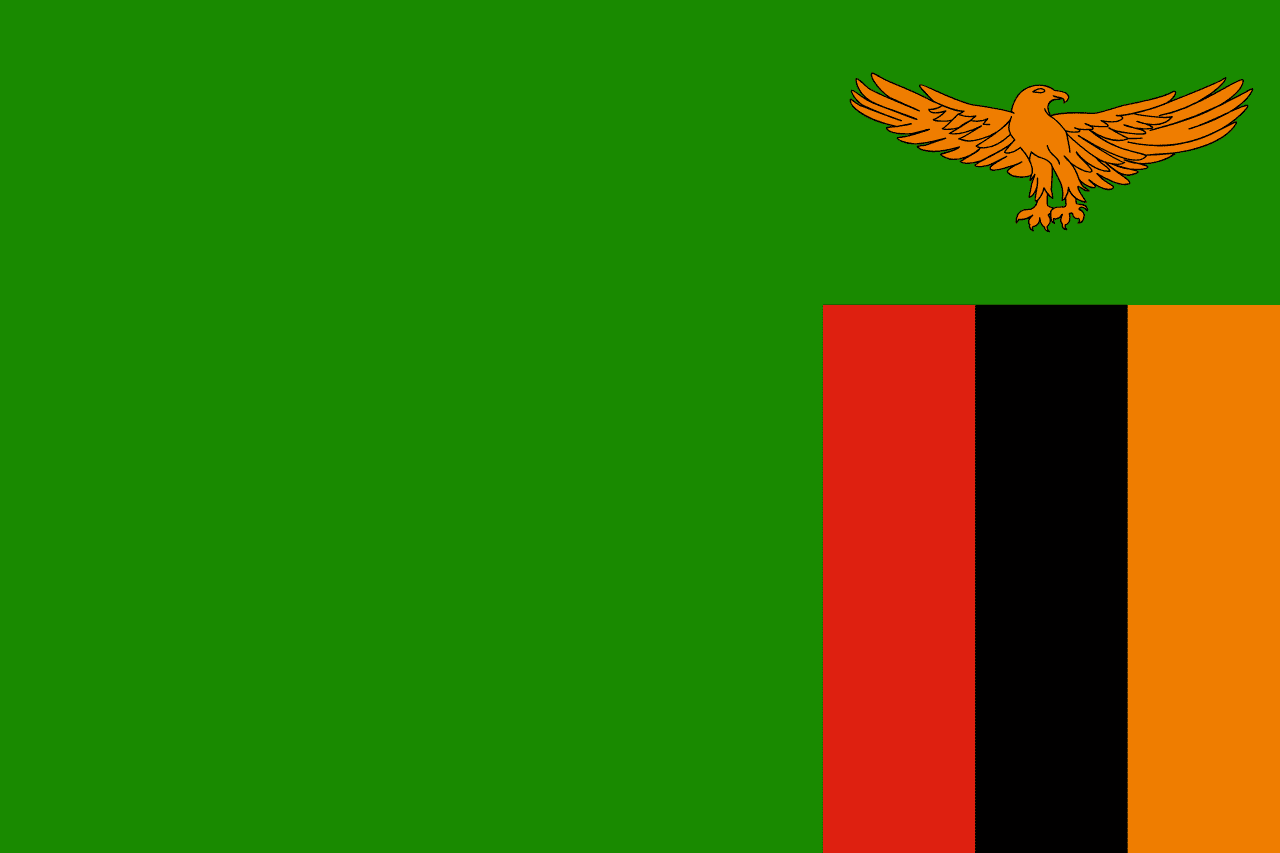
Zambia
Africa
A green field with three vertical stripes of red, black, and orange in the lower right corner and an orange eagle above the stripes, representing the country's natural wealth, the struggle for freedom, the African heritage, the mineral wealth (particularly copper), and the ability to rise above problems.