Sweden Flag Meaning
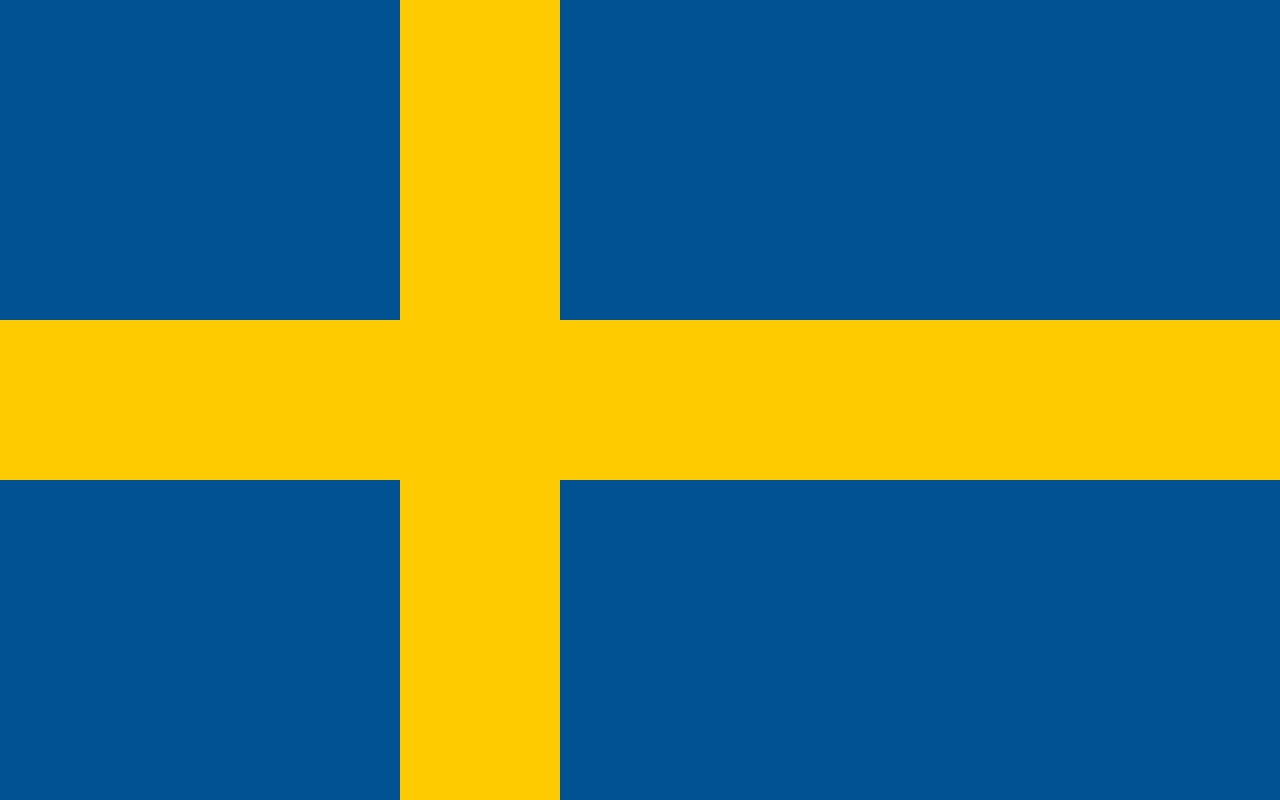
A blue field with a yellow Nordic cross extending to the flag's edges, representing the Christian heritage that shaped Swedish culture and the national colors that have symbolized Sweden since medieval times, part of the Nordic cross tradition shared with other Scandinavian countries.
- Continent
- Europe
- Adopted
- 1906
- Ratio
- 5:8
- Colors
- blue, yellow
- Designer
- Unknown (ancient origins)

Symbolism
Blue Field: Represents loyalty, truth, justice, and the clear blue skies and waters of Sweden, symbolizing the numerous lakes, rivers, and coastal waters that define the Swedish landscape and national character.
Yellow Cross: Represents generosity and the Christian faith that shaped Swedish history and culture, symbolizing the gold and prosperity of the nation as well as the light that guides Sweden through its long winter darkness.
Nordic Cross: Represents the Christian heritage shared with other Nordic countries and the historical connections between Denmark, Norway, Iceland, and the Faroe Islands in the Scandinavian cultural sphere.
Cross Position: The cross is positioned toward the hoist side following the Nordic tradition, creating a distinctive asymmetrical design that unifies the Scandinavian nations under shared symbols and heritage.
History
- 8th-11th Century: Viking Age Sweden saw Norsemen raid and trade across Europe, establishing trade routes to Byzantium and founding settlements from Iceland to Russia, while gradually converting to Christianity.
- 12th-14th Century: The medieval Kingdom of Sweden was established with Christianity becoming dominant, the nobility gaining power, and territorial expansion including parts of Finland under Swedish rule.
- 1397-1523: The Kalmar Union united Denmark, Norway, and Sweden under Danish rule, though Swedish resistance eventually led to independence under Gustav Vasa in 1523.
- 1611-1718: The Swedish Empire reached its zenith under kings like Gustavus Adolphus and Charles XII, controlling territories around the Baltic Sea and playing a major role in European warfare.
- 1809: Sweden lost Finland to Russia and adopted a new constitution that limited royal power, beginning the transformation toward constitutional monarchy and parliamentary government.
- 1814-1905: The union with Norway was established after the Napoleonic Wars, giving Sweden control over its western neighbor until Norwegian independence in 1905.
- June 22, 1906: The current flag design was officially adopted, standardizing the blue and yellow colors and Nordic cross pattern that had been used in various forms for centuries.
- 1914-1945: Sweden maintained neutrality during both world wars, though this was tested by German pressure and demands for transit rights during World War II.
- 1932-1976: Social Democratic dominance created the 'Swedish model' of democratic socialism with extensive welfare state, high taxes, and labor-management cooperation that became internationally famous.
- 1995: Sweden joined the European Union after a narrow referendum victory, though it chose to maintain its own currency rather than adopt the euro.
- 2000s-Present: Sweden has faced challenges with immigration integration, the rise of populist parties, and balancing its generous welfare state with global economic competition.
Trivia
- Sweden is the birthplace of many global brands including IKEA, Volvo, Saab, H&M, Spotify, and Skype, demonstrating the country's innovation and design excellence.
- The flag represents the home of the Nobel Prize, established by Alfred Nobel's will and awarded annually in Stockholm and Oslo for achievements in science, literature, and peace.
- Sweden has one of the world's most comprehensive welfare states, with universal healthcare, free education through university, and generous parental leave and social benefits.
- The country is famous for its pop music, producing global stars like ABBA, Roxette, Ace of Base, and more recently artists like Robyn and Swedish House Mafia.
- Swedish is the official language and is closely related to Norwegian and Danish, though most Swedes speak excellent English due to early language education and media exposure.
- The flag flies over a country that pioneered many environmental policies and has set ambitious goals for carbon neutrality, becoming a leader in sustainable development.
- Sweden has a unique 'Right to Roam' (Allemansrätten) that allows public access to private land for recreation, reflecting the cultural values of equality and nature appreciation.
- The country is home to distinctive design traditions emphasizing functionality, simplicity, and accessibility, exemplified by IKEA furniture and Swedish architecture.
- Traditional Swedish celebrations include Midsummer (summer solstice), Lucia Day (December 13), and crayfish parties, reflecting the importance of seasonal cycles in northern latitudes.
- Sweden has produced many internationally renowned authors including Astrid Lindgren (Pippi Longstocking), Stieg Larsson (Millennium trilogy), and August Strindberg.
- The flag represents a country with extensive forests covering about 70% of the land area, making Sweden a major producer of paper, pulp, and wood products.
- Swedish cuisine includes traditional dishes like meatballs, gravlax, herring, and cinnamon buns, though modern Swedish cooking has gained international recognition for innovation.
- The country has one of the world's most gender-equal societies, with high female workforce participation, generous parental leave for both parents, and progressive social policies.
- Sweden faces unique challenges including an aging population, integration of recent immigrants, and maintaining its welfare model amid economic globalization.
- Despite its peaceful modern image, Sweden has a strong defense industry and maintains military neutrality while cooperating closely with NATO and EU security initiatives.
Related Countries
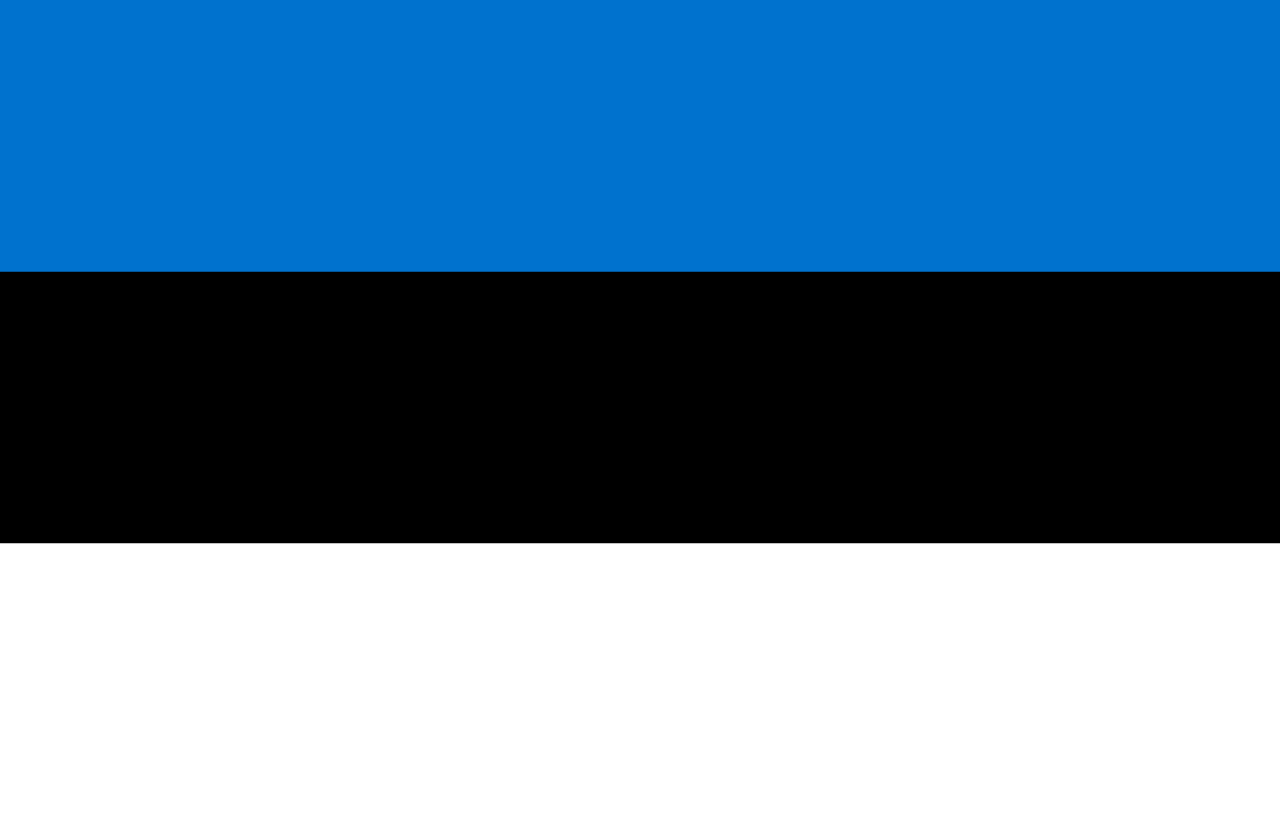

Estonia
Europe
Three horizontal stripes of blue, black, and white representing the sky and sea, the soil and past struggles, and the snow and bright future of this Baltic nation known for its digital innovation and preserved medieval heritage.
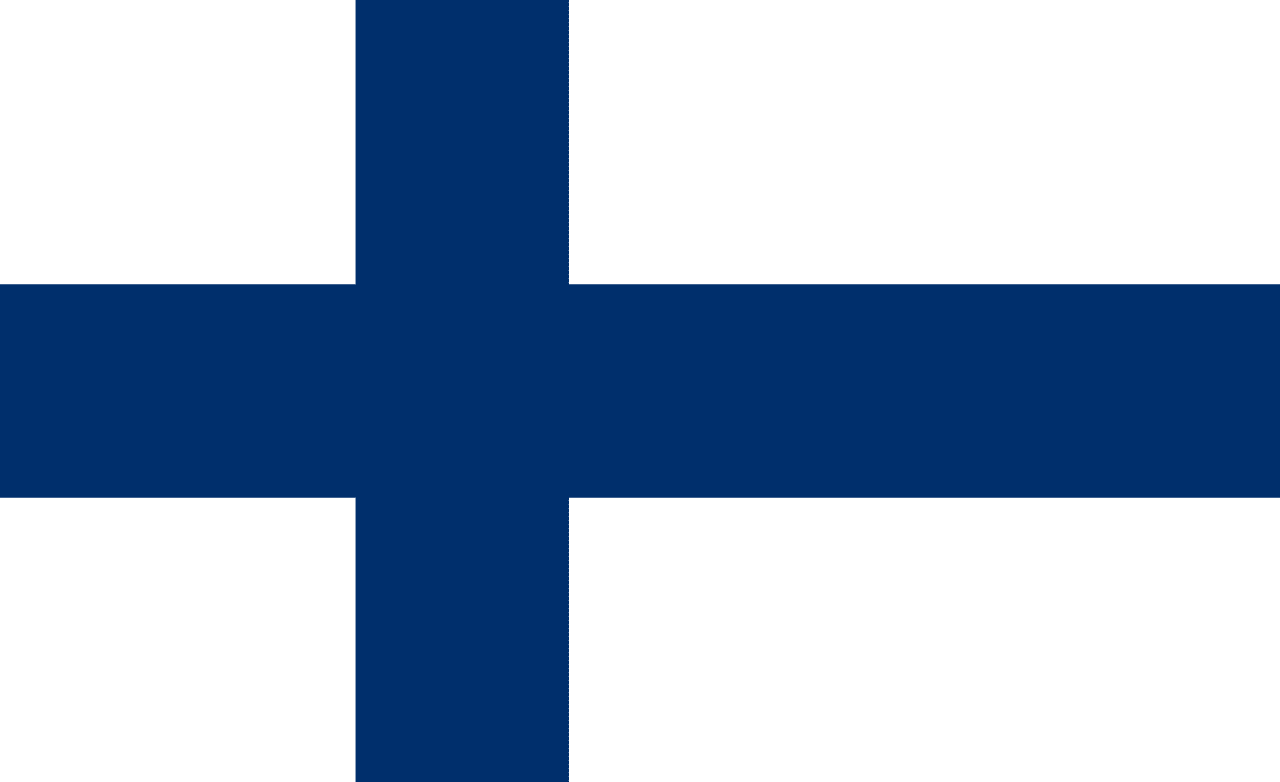

Finland
Europe
A white field with a blue Nordic cross slightly offset toward the hoist, representing Finland's Nordic heritage, the blue lakes and sky, and the white snow that covers the land for much of the year in the 'Land of a Thousand Lakes.'
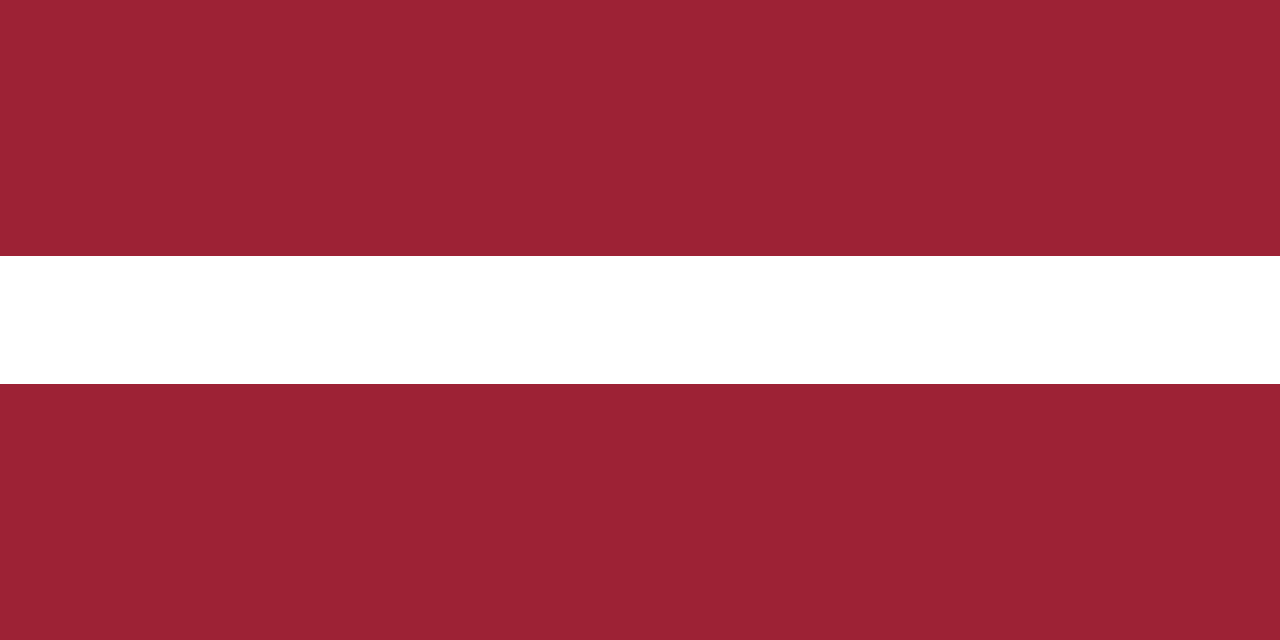

Latvia
Europe
Three horizontal stripes with dark red (maroon) stripes on top and bottom and a narrow white stripe in the center, representing one of the world's oldest flag designs dating back to medieval times and Latvia's struggle for independence.
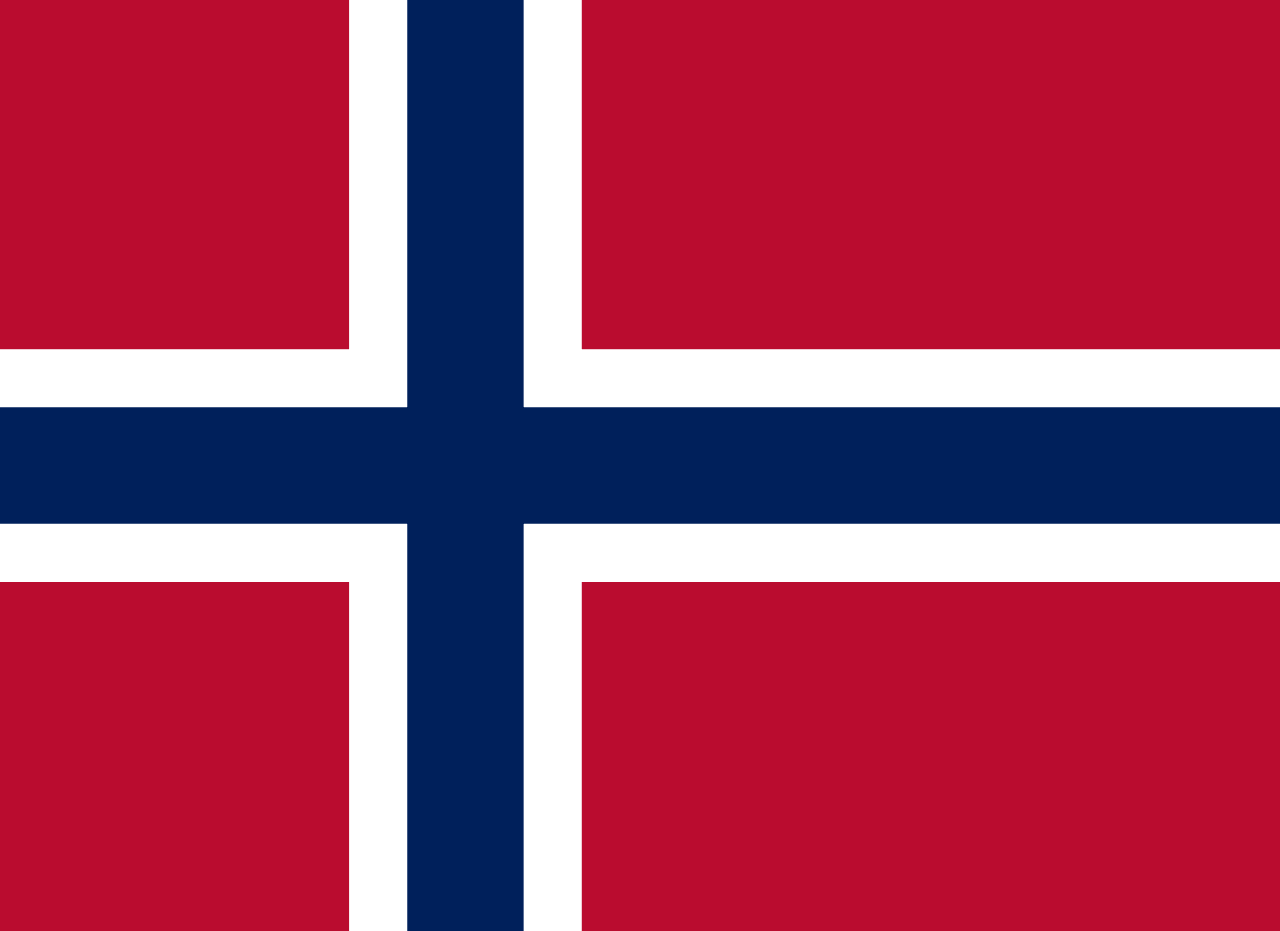
Norway
Europe
Nordic cross design with red field, white cross, and blue outline, symbolizing Norwegian independence and Scandinavian heritage.
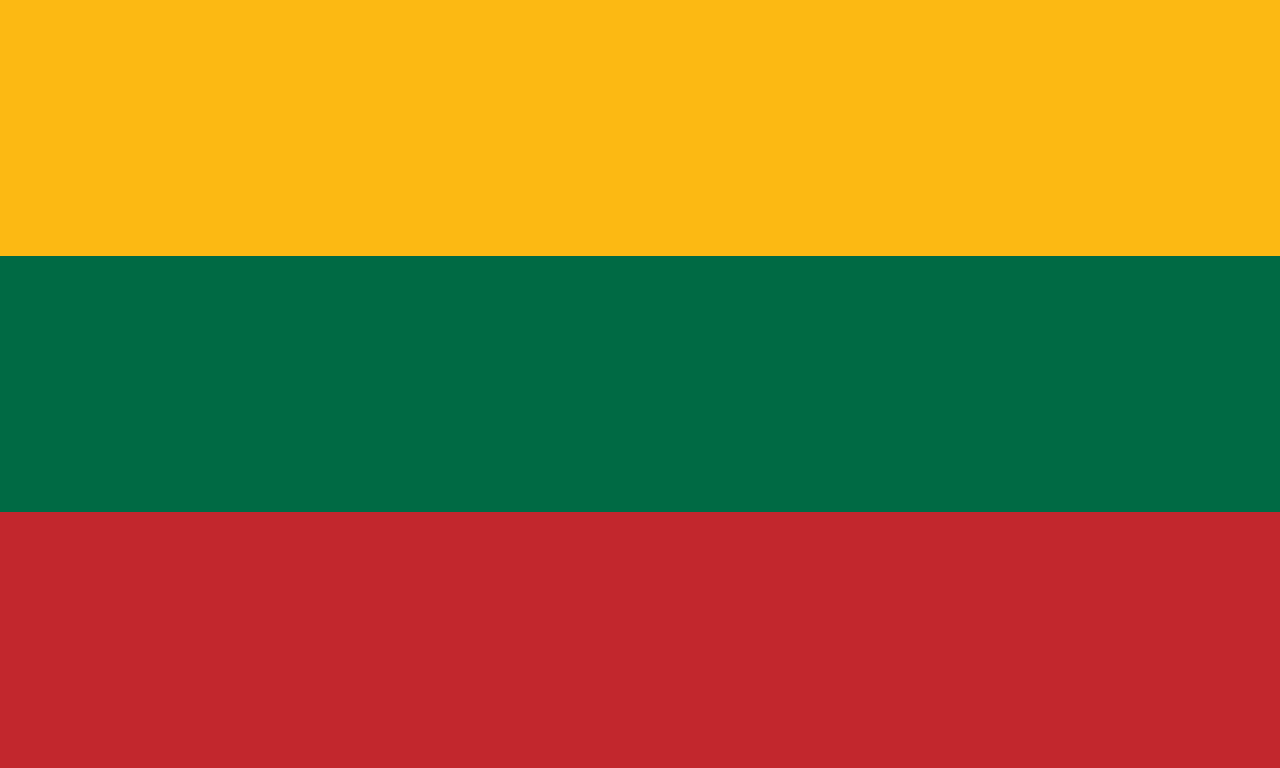

Lithuania
Europe
Three horizontal stripes of yellow, green, and red representing the golden wheat fields, green forests, and blood shed for independence of this Baltic nation that led the peaceful dissolution of the Soviet Union.
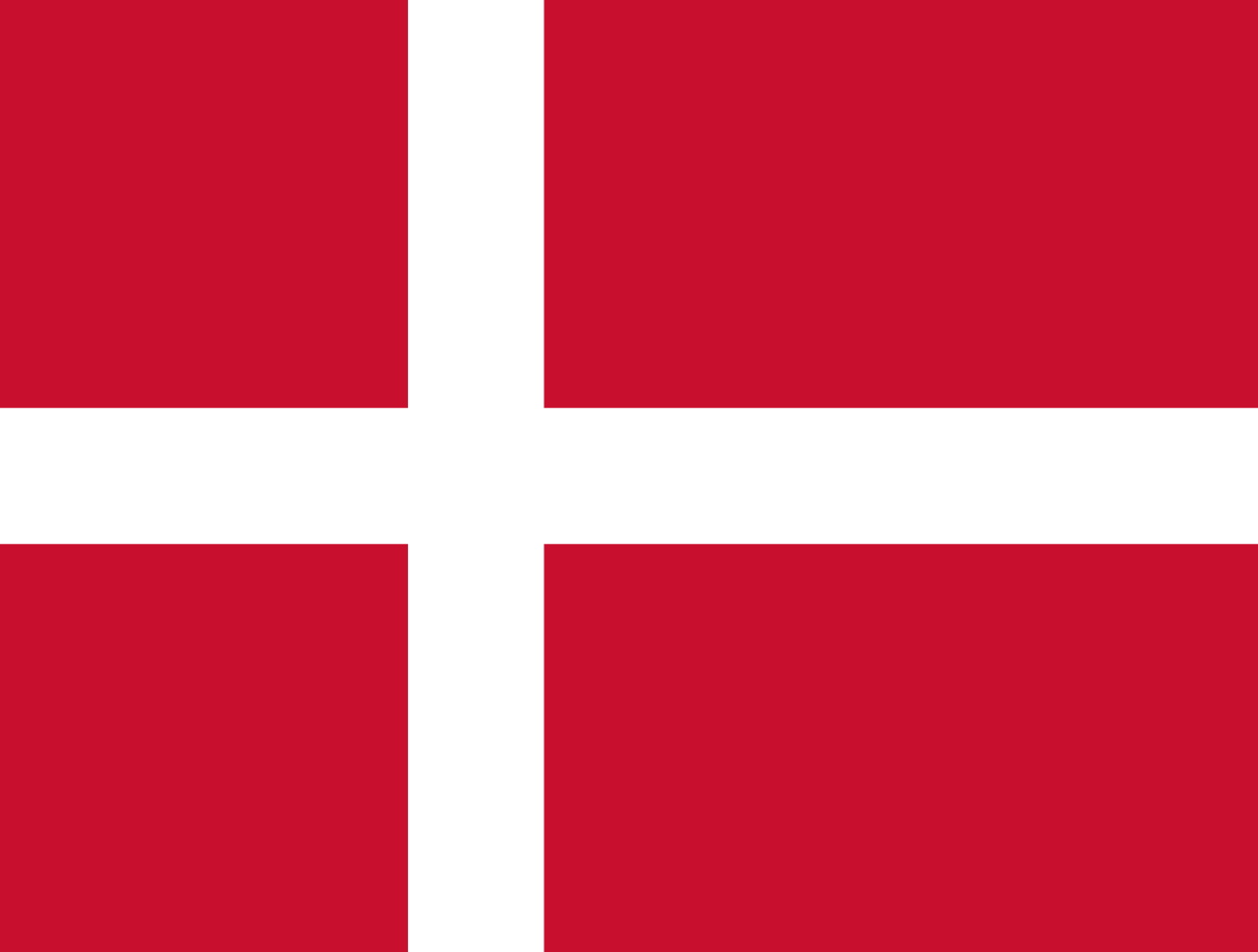
Denmark
Europe
A red field with a white Nordic cross slightly offset toward the hoist, known as the Dannebrog, representing one of the world's oldest national flags and the Christian heritage of the Danish kingdom.