Iraq Flag Meaning
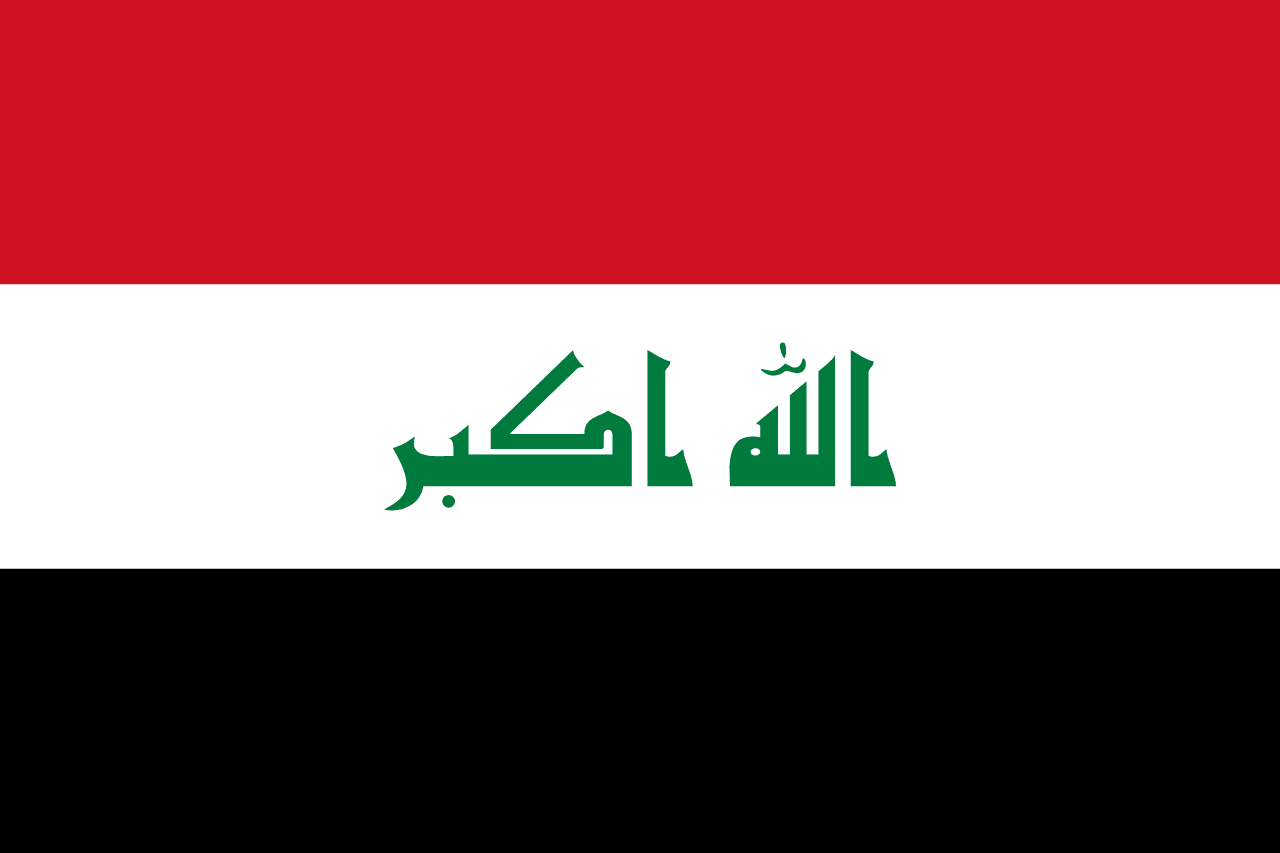
Three horizontal stripes of red, white, and black (Pan-Arab colors) with 'Allahu Akbar' (God is Greatest) written in green Arabic Kufic script across the white stripe, representing Arab unity, Islamic faith, and Iraqi sovereignty.
- Continent
- Asia
- Adopted
- 2008
- Ratio
- 2:3
- Colors
- red, white, black, green
- Designer
- Iraqi Parliament (current version)

Symbolism
Red Stripe: Represents the blood shed by Iraqi martyrs in their struggle for independence and freedom, symbolizing courage, sacrifice, and the determination of the Iraqi people throughout their history of resistance and liberation.
White Stripe: Represents peace, purity, and the bright future of Iraq, symbolizing the hope for national unity, tolerance among different communities, and the aspiration for stability and prosperity.
Black Stripe: Represents the dark period of oppression and foreign occupation that Iraq has endured, symbolizing the overcoming of hardship and the strength derived from surviving difficult historical periods.
Green Arabic Text: The phrase 'Allahu Akbar' (God is Greatest) written in green Kufic script represents the Islamic faith of the majority of Iraqis and serves as an expression of divine guidance and spiritual foundation for the nation.
History
- 1921-1958: The Kingdom of Iraq used various flags featuring the Hashemite Arab Revolt colors, reflecting the monarchy established by the British with Faisal I as king and the Pan-Arab nationalist movement.
- July 14, 1958: The Iraqi Revolution overthrew the monarchy, and the new republic adopted a flag with vertical stripes of black, white, and green with a red triangle, marking the end of royal rule.
- 1963-1991: Iraq adopted the Pan-Arab colors in horizontal stripes with three green stars representing the proposed union with Egypt and Syria, reflecting Ba'ath Party ideology and Arab nationalist aspirations.
- January 1991: During the Gulf War, Saddam Hussein added 'Allahu Akbar' in green Arabic script between the stars, claiming to invoke divine support and appeal to religious sentiment during the conflict.
- 2004: After the US-led invasion and fall of Saddam Hussein, the Iraqi Interim Government temporarily modified the flag design while maintaining the basic Pan-Arab color scheme.
- 2008: The current flag was adopted by the Iraqi Parliament, removing the three stars and keeping 'Allahu Akbar' in stylized Kufic script, representing the new democratic Iraq's Islamic identity.
Trivia
- Iraq is home to ancient Mesopotamia, often called the 'Cradle of Civilization,' where writing, the wheel, and the first cities were developed around 3500 BCE.
- The flag flies over the land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, where the biblical Garden of Eden is traditionally believed to have been located.
- Baghdad, Iraq's capital, was once the largest city in the world during the Islamic Golden Age and the center of the House of Wisdom, a major intellectual center.
- Iraq contains numerous UNESCO World Heritage Sites, including the ancient city of Babylon and the Assyrian capital of Nineveh.
- The flag represents a country with the world's fifth-largest proven oil reserves, making petroleum the backbone of Iraq's economy.
- Iraq is the birthplace of Abraham according to Jewish, Christian, and Islamic traditions, with Ur being located in modern-day southern Iraq.
- The flag flies over a country where Arabic and Kurdish are both official languages, reflecting Iraq's diverse ethnic composition.
- Iraq's flag represents a nation that is home to important Shia Islamic holy sites, including the shrines in Najaf and Karbala, attracting millions of pilgrims annually.
- The ancient city of Ur, home to the famous Ziggurat, lies in Iraq, representing one of humanity's earliest urban civilizations.
- Iraq's marshlands in the south are believed to be the location of the biblical flood narrative and were once home to the unique Marsh Arab culture.
- The flag represents a country that was the center of the Abbasid Caliphate from 750-1258 CE, during which Baghdad was the cultural and scientific capital of the Islamic world.
- Iraq has a rich tradition of poetry and literature, with the flag representing the homeland of many renowned Arab poets and scholars throughout history.
- The country is home to the ancient Library of Ashurbanipal in Nineveh, which contained the world's first organized library with over 30,000 cuneiform tablets.
- Iraq's flag flies over a land where chess is believed to have been first played, and where many mathematical and astronomical discoveries were made during the Islamic Golden Age.
- The flag represents a country working to rebuild its cultural heritage after conflicts, with efforts to restore and protect its numerous archaeological sites and museums.
Related Countries
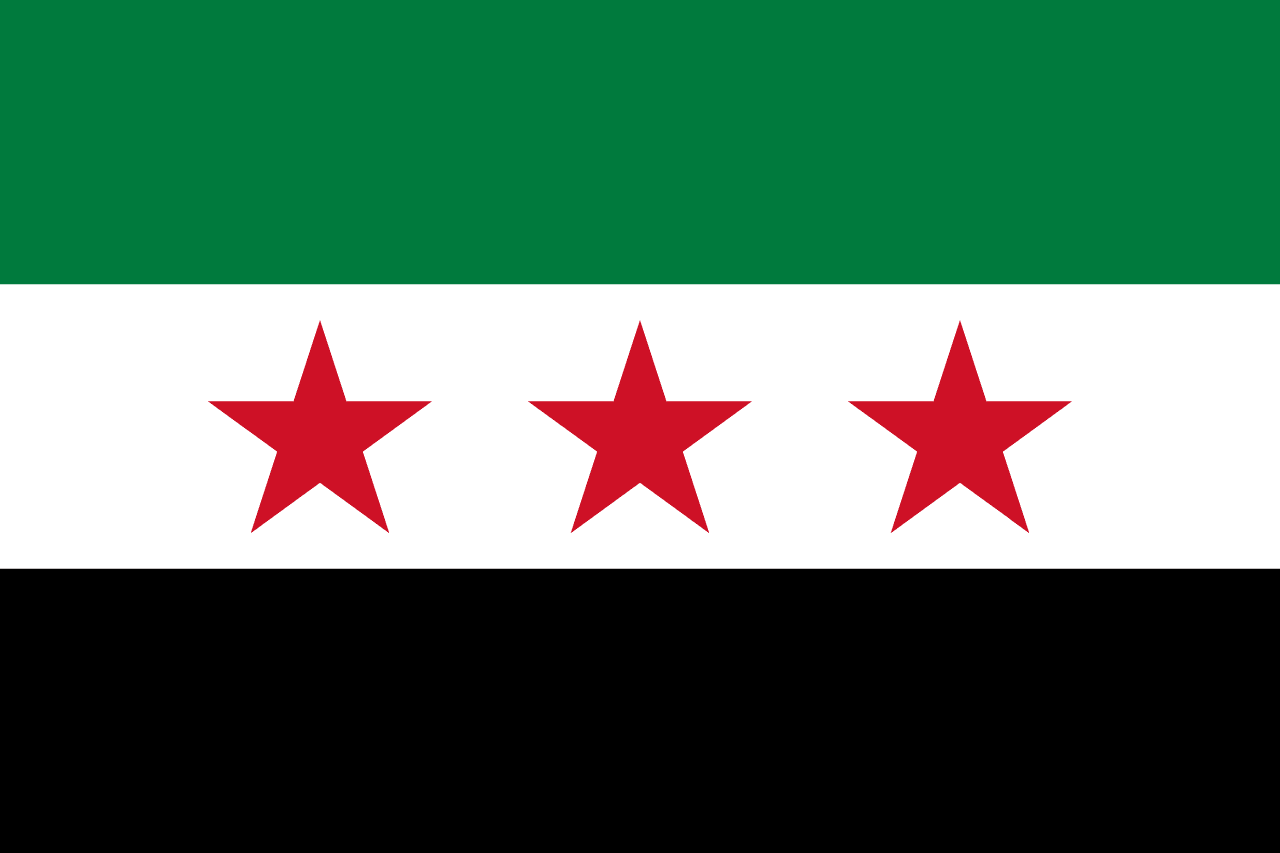

Syria
Asia
Three horizontal stripes of red, white, and black with two green five-pointed stars on the white stripe, representing the Pan-Arab colors of liberation struggles, the Hashemite flag heritage, and the Ba'ath Party's Arab socialist ideology that has governed Syria since 1963.
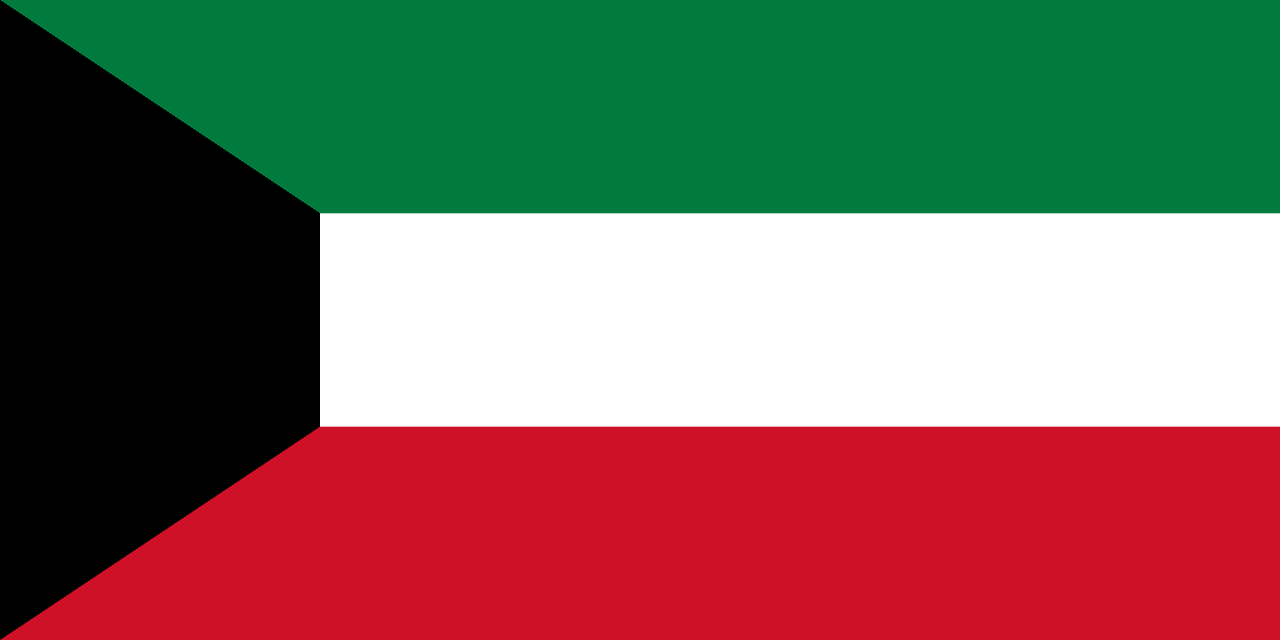

Kuwait
Asia
Three horizontal stripes of green, white, and red with a black trapezoid on the hoist side, representing Kuwait's position in the Arab world and its transformation from pearl diving to oil wealth in the Arabian Gulf.

Lebanon
Asia
Two horizontal red stripes separated by a white stripe twice their width, with a green cedar tree centered on the white stripe, representing the strength, purity, and eternal heritage of the 'Land of the Cedars.'

Jordan
Asia
Three horizontal stripes of black, white, and green with a red triangle on the hoist side containing a seven-pointed white star, representing the Arab Revolt heritage and the Hashemite Kingdom's role as guardian of Islamic holy sites.
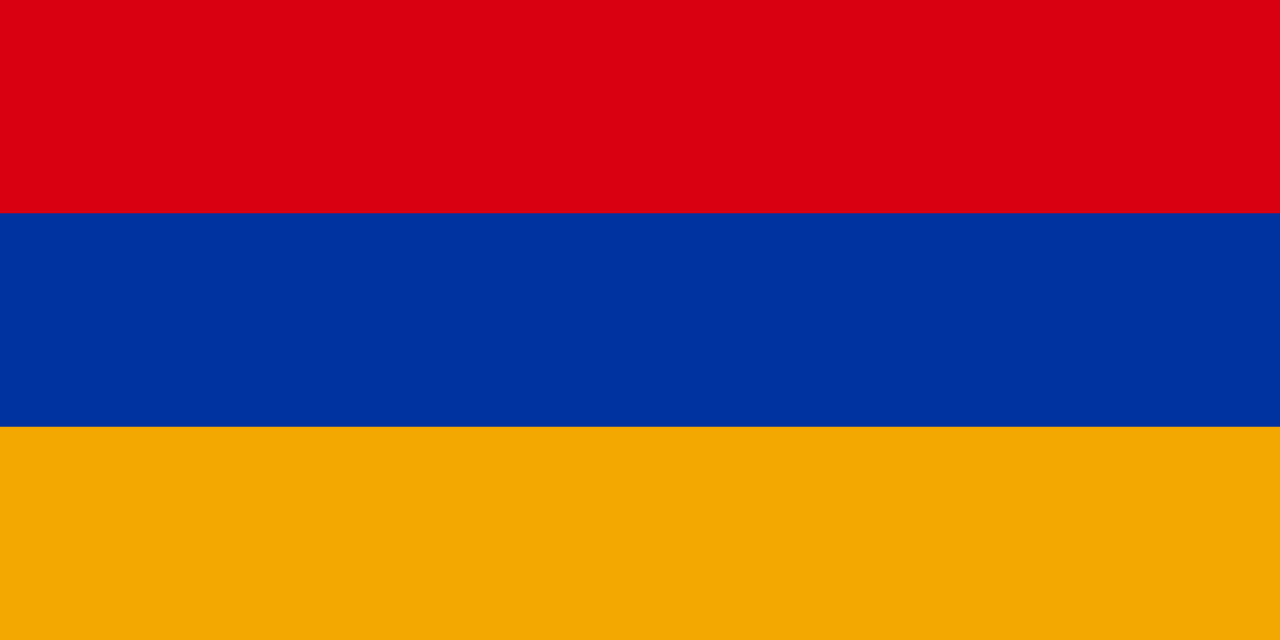

Armenia
Asia
Three horizontal stripes of red, blue, and orange (apricot), representing the blood shed for independence, the Armenian sky and hope for peace, and the fertile land and hardworking nature of the Armenian people, based on the flag of the First Republic of Armenia (1918-1920).
Azerbaijan
Asia
Three horizontal stripes of blue, red, and green with a white crescent and eight-pointed star in the center, representing Turkic heritage, modernity and progress, Islamic tradition, and the eight branches of the Turkic peoples, designed during the brief independence period of 1918-1920.