Gambia Flag Meaning
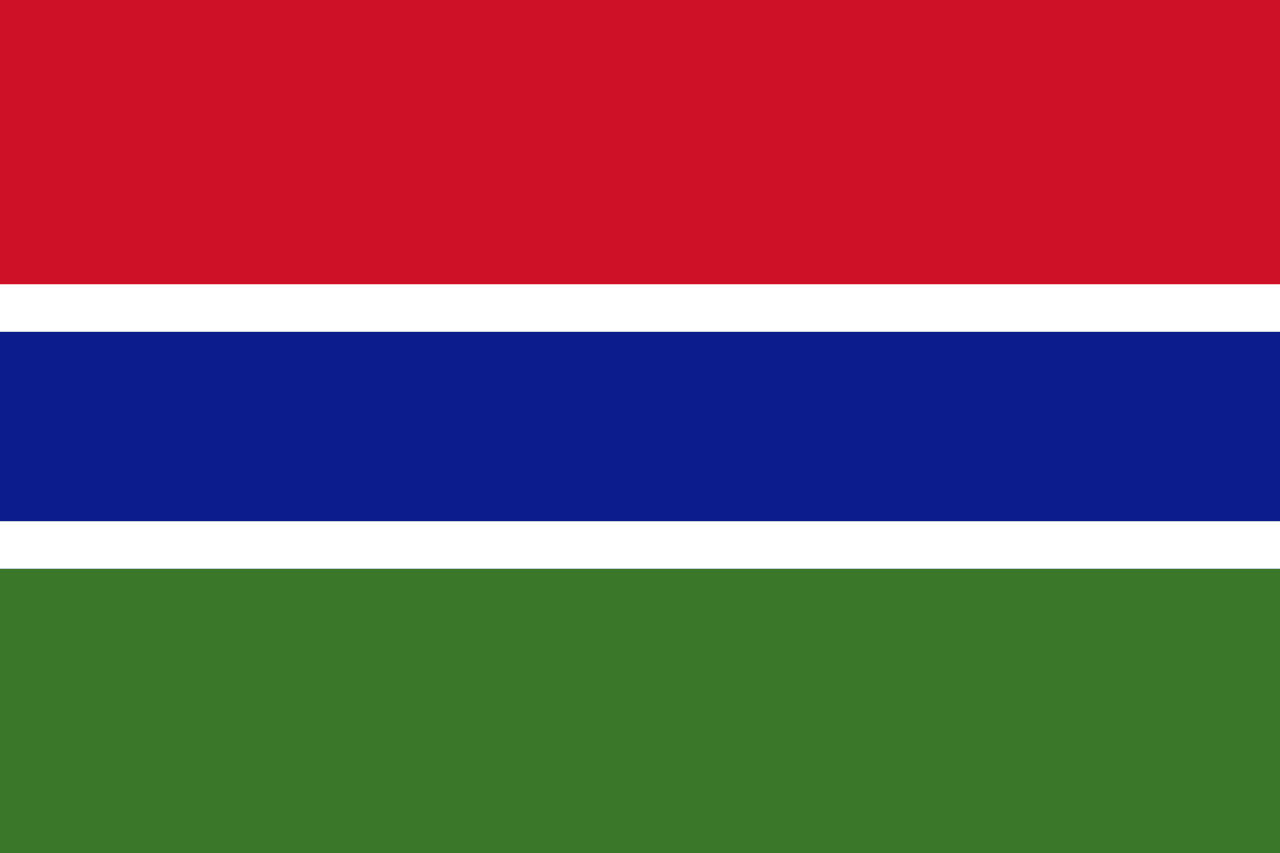
Three horizontal stripes of red, blue, and green separated by thin white stripes, representing the sun, the Gambia River, agriculture, and peace, symbolizing the natural beauty and harmony of the smallest mainland African nation.
- Continent
- Africa
- Adopted
- 1965
- Ratio
- 2:3
- Colors
- red, white, blue, green
- Designer
- Pa Louis Thomasi

Symbolism
Red Stripe: Represents the sun that shines over Gambia and the equatorial heat of the West African climate, symbolizing the energy, vitality, and warmth of the Gambian people and their determination to build their nation.
Blue Stripe: Represents the Gambia River, which flows through the entire length of the country and gives it its name, symbolizing the life-giving waters that sustain agriculture, transportation, and the livelihood of the Gambian people.
Green Stripe: Represents the land, agriculture, and forests of Gambia, symbolizing the fertility of the soil, the importance of farming to the economy, and the country's commitment to environmental conservation.
White Stripes: Represent peace and unity among the diverse ethnic groups of Gambia, symbolizing harmony, tolerance, and the desire for peaceful coexistence in the multi-ethnic Gambian society.
History
- Pre-1455: The region was part of great West African empires including Ghana, Mali, and Songhai, with various ethnic groups including Mandinka, Wolof, and Fula establishing trading settlements along the Gambia River.
- 1455-1783: Portuguese exploration was followed by British and French competition for control of the river trade, with various European trading posts established for the gold, ivory, and later slave trades.
- 1783-1965: British colonial rule was established with the colony of Gambia, centered on Bathurst (now Banjul), with the Union Jack representing colonial administration over the river territory and its peoples.
- 1960s: The independence movement gained momentum under leaders like David Jawara, with negotiations for self-government and the development of national symbols in preparation for independence.
- February 18, 1965: Gambia gained independence from Britain as a constitutional monarchy within the Commonwealth, adopting the current flag designed by Pa Louis Thomasi to represent the new sovereign nation.
- April 24, 1970: Gambia became a republic, maintaining the same flag while establishing a new constitution and confirming its identity as an independent West African state.
- 1994-2017: A military coup brought Yahya Jammeh to power, ruling as an increasingly authoritarian leader while the flag continued to represent hopes for democracy and human rights.
- 2017-Present: The democratic transition following Adama Barrow's election victory restored constitutional governance, with the flag representing renewed hopes for democracy, development, and regional integration.
Trivia
- Gambia is the smallest country in mainland Africa, roughly the size of Connecticut, and is almost entirely surrounded by Senegal except for its Atlantic coastline.
- The flag represents a country that is shaped like a finger, following the course of the Gambia River for about 300 miles inland from the Atlantic Ocean.
- Gambia and Senegal briefly formed the confederation of Senegambia from 1982-1989, though it was dissolved due to political and economic differences.
- The flag flies over a country where the Gambia River is the dominant geographic feature, providing transportation, irrigation, and serving as the basis for the colonial boundaries.
- Banjul, the capital, is built on an island at the mouth of the Gambia River and is one of the smallest capital cities in the world by area.
- The flag represents a country with remarkable biodiversity despite its small size, including over 540 bird species that make it a popular destination for birdwatching tourism.
- Gambia is predominantly Muslim (about 95% of the population), yet maintains religious tolerance and peaceful coexistence among different faiths and ethnic groups.
- The country's economy depends heavily on tourism, agriculture (especially peanuts), and fishing, with the flag representing these natural resource-based livelihoods.
- Gambia has never experienced a civil war, making it relatively peaceful compared to some of its West African neighbors, despite political challenges.
- The flag flies over a country where English is the official language, but local languages including Mandinka, Wolof, and Fula are widely spoken.
- Kunta Kinteh Island (formerly James Island) is a UNESCO World Heritage Site that serves as a memorial to the Atlantic slave trade and its impact on Africa.
- The flag represents a country where groundnuts (peanuts) are a major export crop, continuing a tradition that began during the colonial period.
- Gambia's beaches along the Atlantic coast are a major tourist attraction, particularly for Europeans seeking winter sunshine and West African culture.
- The country has a young population with a median age of about 17 years, representing both challenges and opportunities for development under the flag.
- Gambia's recent democratic transition from Yahya Jammeh's 22-year rule to Adama Barrow's presidency was achieved peacefully with regional support, demonstrating the strength of West African diplomatic cooperation.
Related Countries
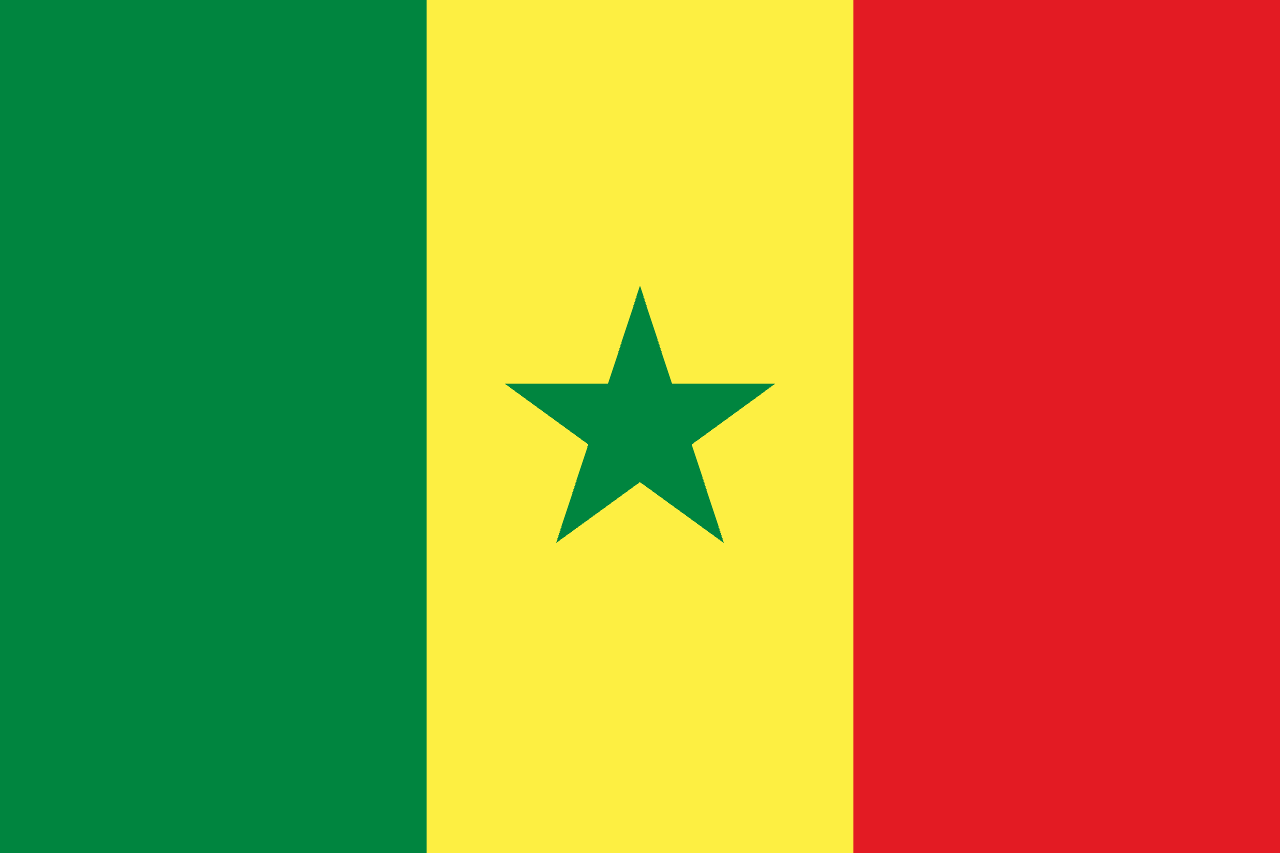

Senegal
Africa
A vertical tricolor of green, yellow, and red with a green five-pointed star centered in the yellow band. The flag reflects Pan-African identity and national unity.
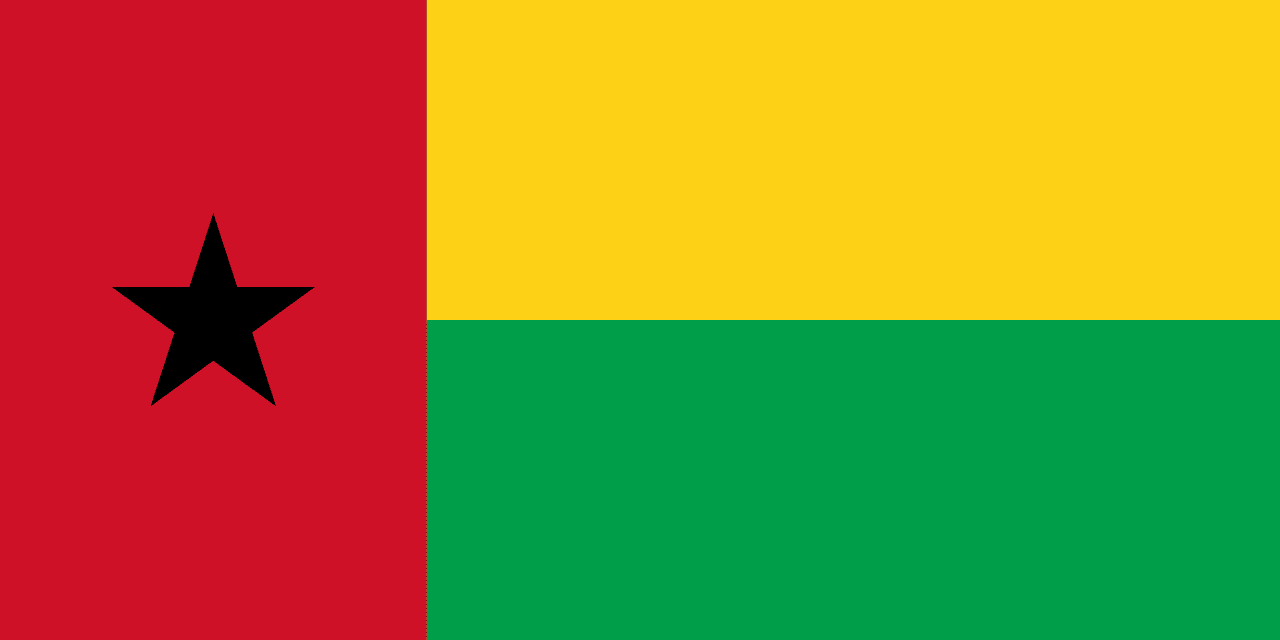

Guinea-Bissau
Africa
A vertical red stripe at the hoist with a black five-pointed star, and two horizontal stripes of yellow over green on the fly side, representing the liberation struggle, unity, hope, and the agricultural wealth of Guinea-Bissau.
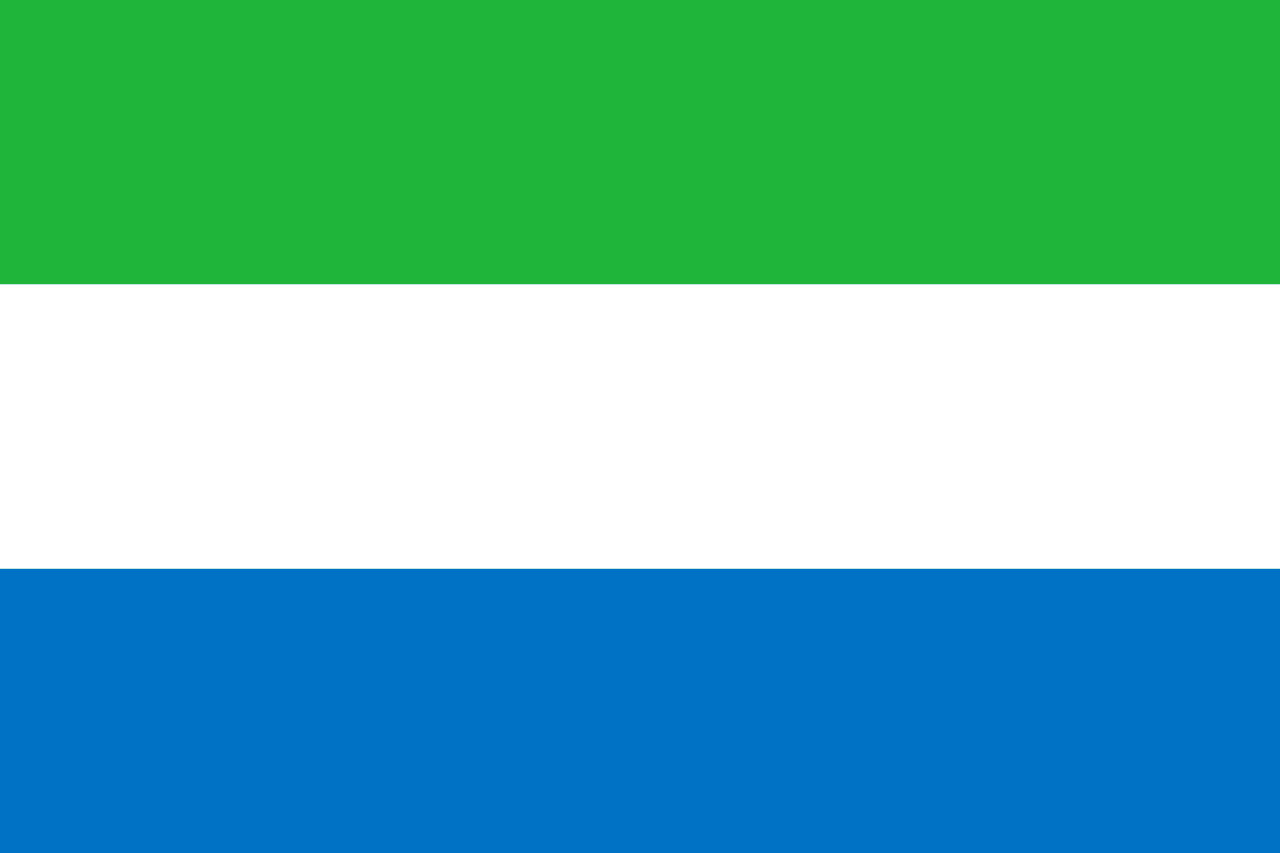

Sierra Leone
Africa
A horizontal tricolor of green, white, and blue, symbolizing the land, unity and justice, and the sea and hope, adopted at independence in 1961.
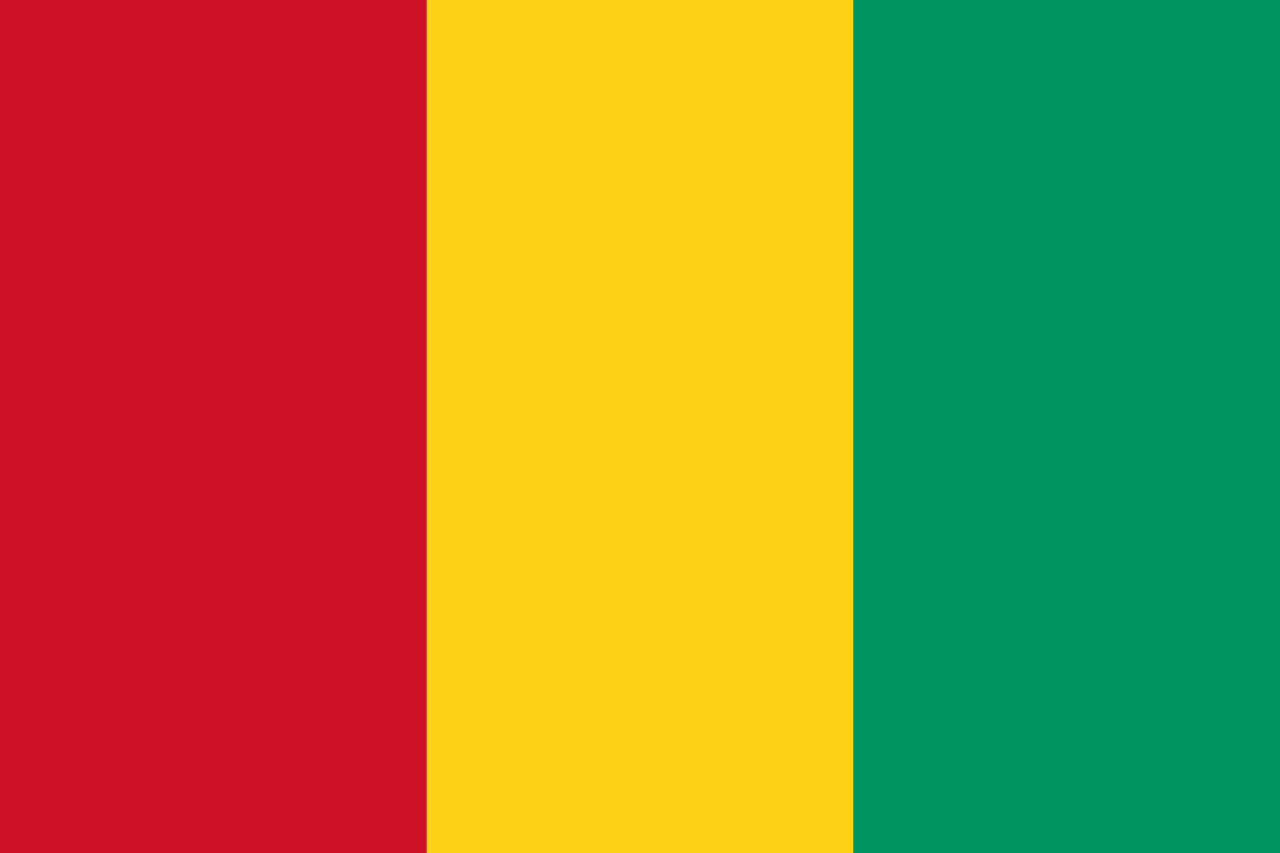

Guinea
Africa
Three equal vertical stripes of red, yellow, and green representing the Pan-African colors, with red symbolizing sacrifice, yellow representing the sun and mineral wealth, and green representing the country's vegetation and agriculture.
Mauritania
Africa
A green field with yellow crescent and star, bordered by red stripes at top and bottom, representing Mauritania's Islamic identity, the Sahara Desert, and the blood of those who defended the nation.
Liberia
Africa
Eleven alternating red and white stripes with a blue canton containing a single white five-pointed star, representing Africa's first republic founded by freed American slaves and its role as a beacon of freedom on the continent.