Denmark Flag Meaning
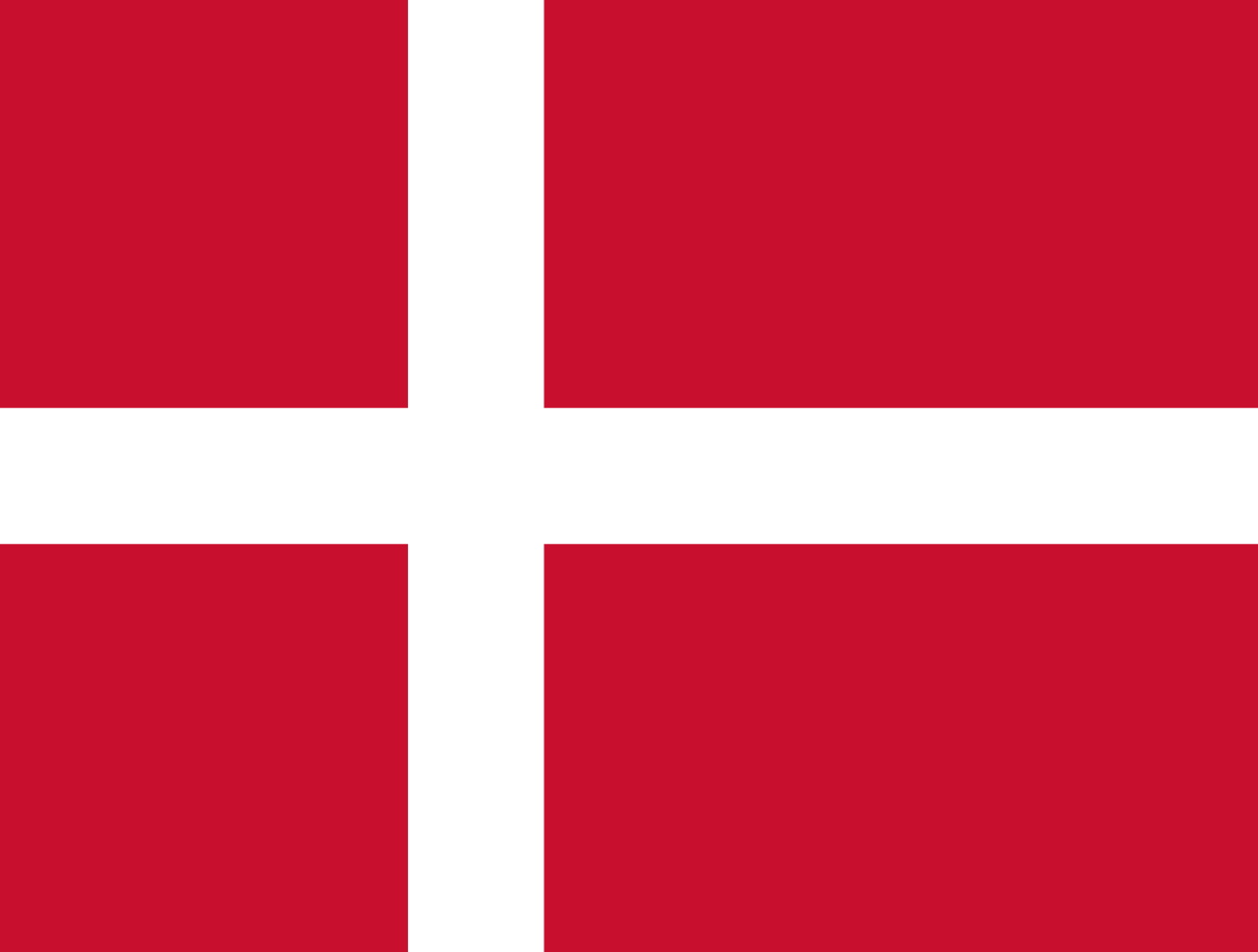
A red field with a white Nordic cross slightly offset toward the hoist, known as the Dannebrog, representing one of the world's oldest national flags and the Christian heritage of the Danish kingdom.
- Continent
- Europe
- Adopted
- 1219
- Ratio
- 28:37
- Colors
- red, white
- Designer
- Unknown (legendary divine origin)
Symbolism
Red Field: Represents the strength, courage, and valor of the Danish people throughout their long history, symbolizing the blood shed in defense of the realm and the passionate spirit of the Viking heritage and Danish monarchy.
White Nordic Cross: Represents Christianity and the Christian faith that has been central to Danish identity since the conversion in the 10th century, symbolizing divine guidance, purity, and the spiritual foundation of Danish civilization.
Cross Design: The Nordic cross design originated with Denmark and spread to other Scandinavian countries, representing the shared cultural and religious heritage of the Nordic region and Denmark's historical influence in Northern Europe.
History
- 960s-1219: Denmark was Christianized under Harald Bluetooth around 960 CE, with various royal banners and symbols used before the legendary appearance of the Dannebrog during the Battle of Lyndanisse in Estonia.
- June 15, 1219: According to legend, the Dannebrog fell from heaven during King Valdemar II's battle against Estonian pagans, turning the tide of battle and establishing the flag as a divine symbol of Danish victory.
- 1219-1397: The Dannebrog became established as the royal and national symbol during Denmark's medieval expansion, representing the powerful Danish kingdom that controlled much of the Baltic Sea region.
- 1397-1523: During the Kalmar Union, the Dannebrog represented Danish leadership of the unified Scandinavian kingdoms of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden under Danish royal authority.
- 1523-1814: The flag represented the Danish-Norwegian dual monarchy, flying over territories from Greenland to the Caribbean, symbolizing one of Europe's significant colonial and maritime powers.
- 1849: Denmark adopted its first democratic constitution, with the Dannebrog transitioning from a royal symbol to representing the constitutional monarchy and democratic Danish nation.
- 1940-1945: During Nazi occupation, the Dannebrog became a symbol of resistance and national identity, with Danes wearing flag pins and displaying the flag as acts of defiance against German occupation.
- 1945-Present: The flag has represented Denmark's development into a modern welfare state, NATO founding member, EU member, and global leader in renewable energy and social democracy.
Trivia
- The Dannebrog is recognized as the world's oldest continuously used national flag, with its basic design unchanged for over 800 years.
- Denmark's flag inspired the design of all other Nordic cross flags, including those of Norway, Sweden, Finland, Iceland, and the Faroe Islands.
- The flag represents the birthplace of LEGO, invented in Denmark in 1958, with the toy company becoming one of the world's most valuable and recognizable brands.
- Denmark consistently ranks as one of the world's happiest countries, with the flag representing the successful Nordic welfare state model and high quality of life.
- The flag flies over the Kingdom of Denmark, which includes Greenland (the world's largest island) and the Faroe Islands, making it a transcontinental realm.
- Denmark is a global leader in wind energy, generating more than 50% of its electricity from wind power and exporting wind turbine technology worldwide.
- Copenhagen, the capital, is famous for its bicycle culture, with more bikes than cars and extensive cycling infrastructure that has influenced urban planning globally.
- The flag represents a country with no mountains, where the highest natural point is only 171 meters above sea level, creating a distinctive flat landscape.
- Denmark has more Michelin-starred restaurants per capita than anywhere except Monaco, with Copenhagen becoming a global culinary destination.
- The Viking Age originated from Denmark and neighboring Scandinavian countries, with Danish Vikings exploring and settling across Europe, from England to Russia.
- Denmark abolished slavery in its colonies in 1848 and has been a leader in social progress, including being the first country to recognize same-sex civil unions in 1989.
- The flag represents a country that invented the concept of hygge, the Danish art of cozy contentment that has become internationally popular as a lifestyle philosophy.
- Denmark's social safety net is among the world's most comprehensive, with free healthcare, education through university, and generous unemployment benefits.
- The Little Mermaid statue in Copenhagen harbor has become an iconic symbol of Denmark, though it's actually quite small compared to its international fame.
- Denmark has more pigs than people, with pork being a major export industry, and Danish bacon and ham being renowned for their quality worldwide.
Related Countries
Norway
Europe
Nordic cross design with red field, white cross, and blue outline, symbolizing Norwegian independence and Scandinavian heritage.
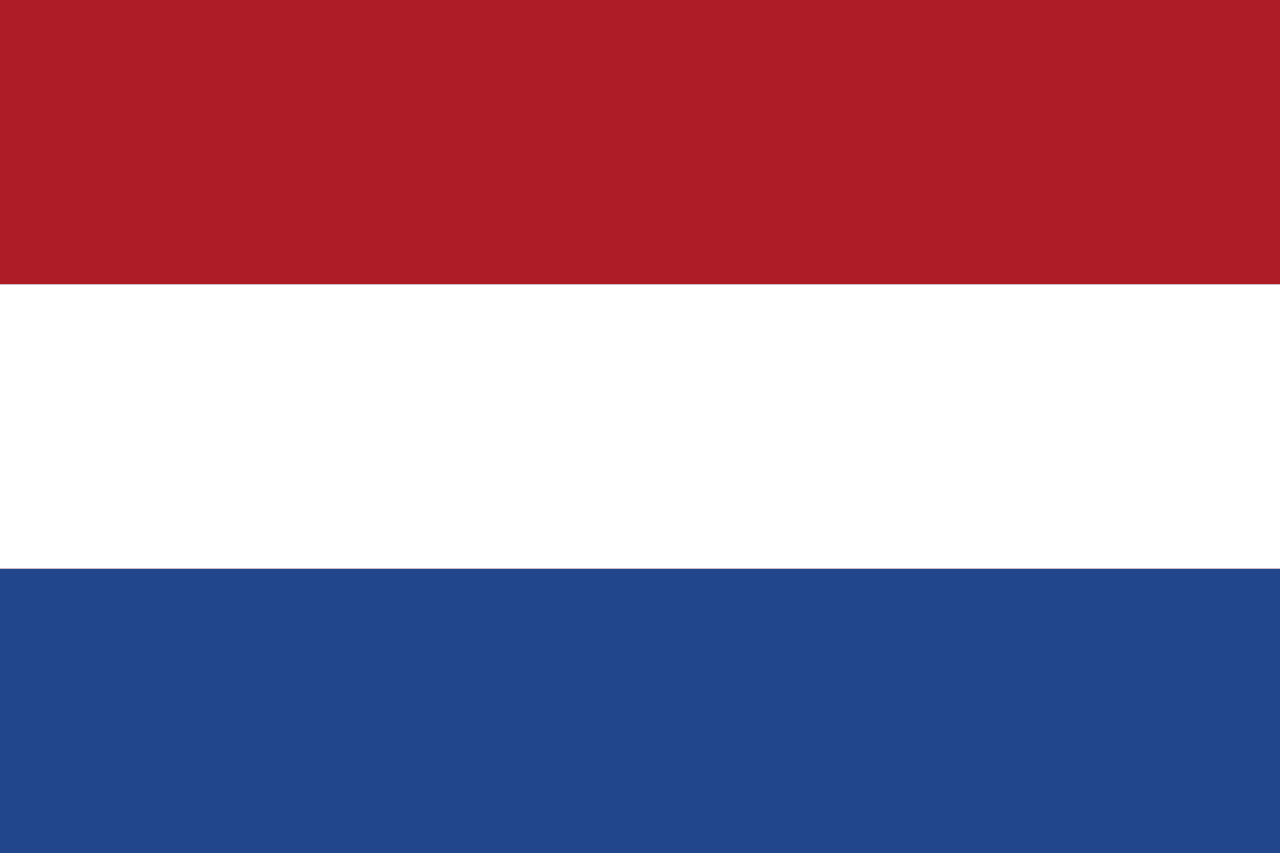

Netherlands
Europe
A horizontal tricolor of red, white, and blue, the oldest tricolor still in use today. It originated in the 16th century during the Dutch Revolt against Spain.
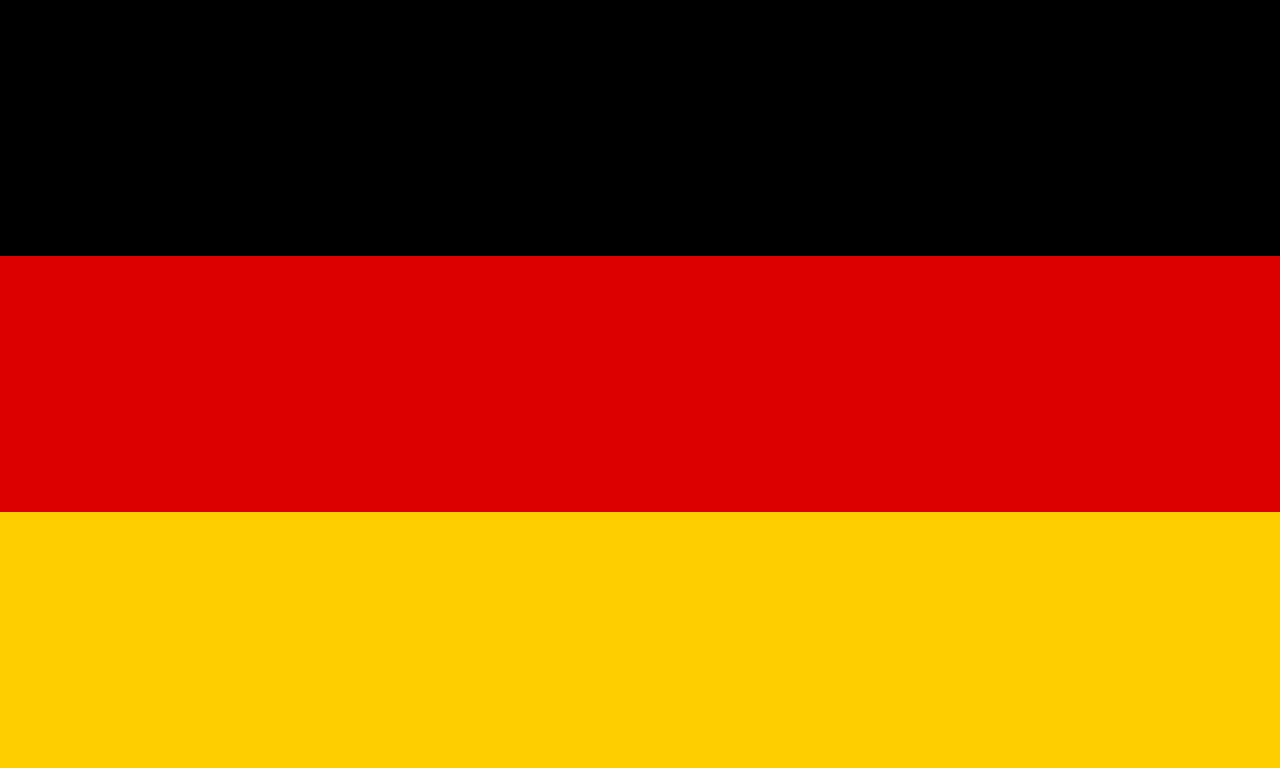

Germany
Europe
Three horizontal stripes of black, red, and gold representing the democratic traditions of Germany, with colors rooted in the 19th-century liberal movement and symbolizing unity, justice, and freedom in the modern Federal Republic.
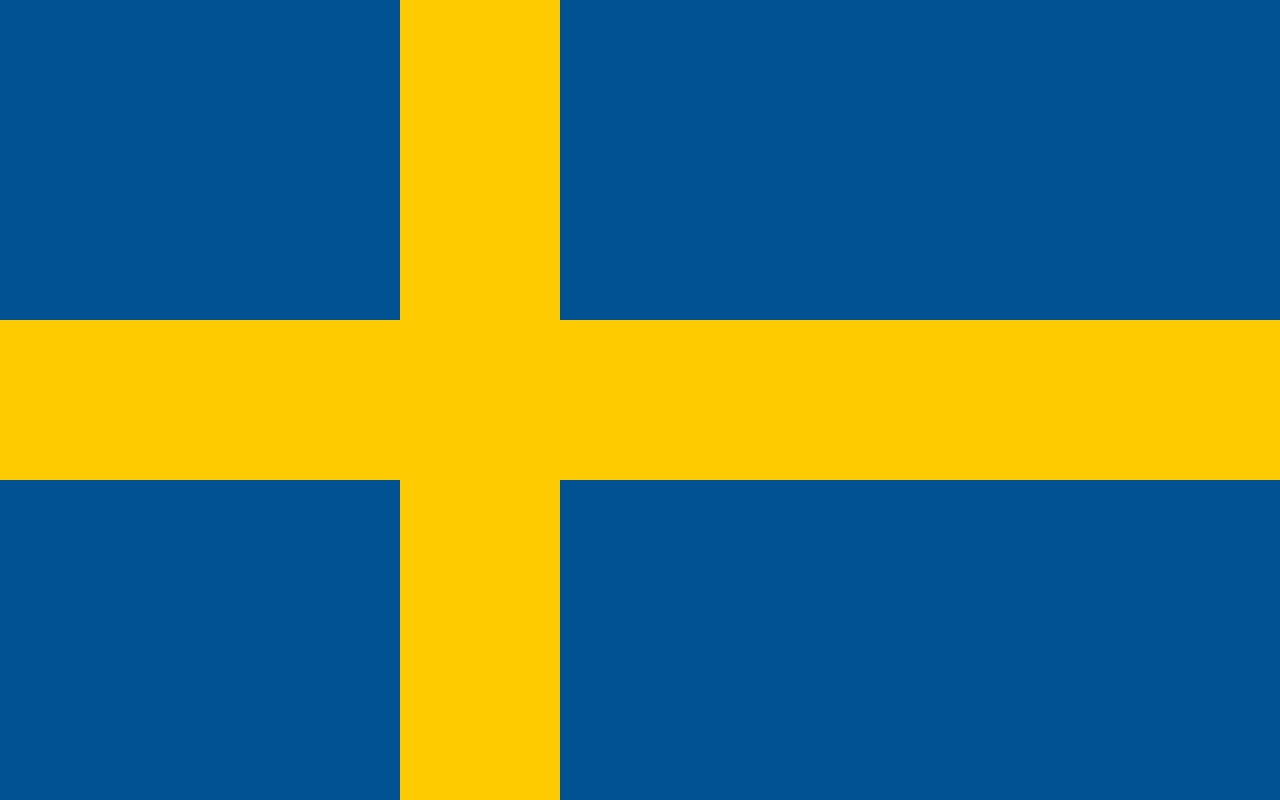

Sweden
Europe
A blue field with a yellow Nordic cross extending to the flag's edges, representing the Christian heritage that shaped Swedish culture and the national colors that have symbolized Sweden since medieval times, part of the Nordic cross tradition shared with other Scandinavian countries.
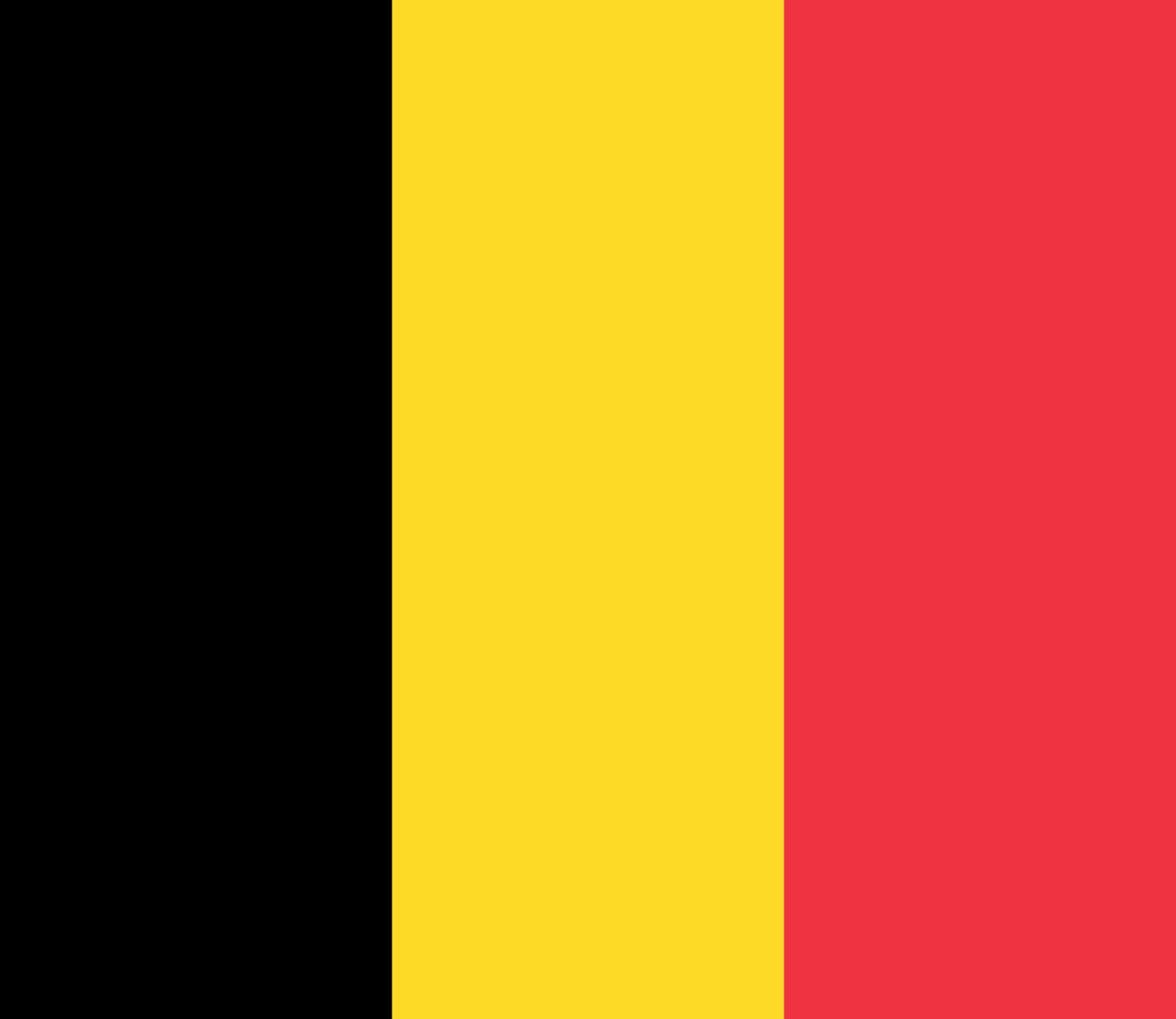

Belgium
Europe
Three vertical stripes of black, yellow, and red derived from the coat of arms of the Duchy of Brabant, adopted during Belgium's independence revolution and representing the nation's determination, generosity, and sacrifice.
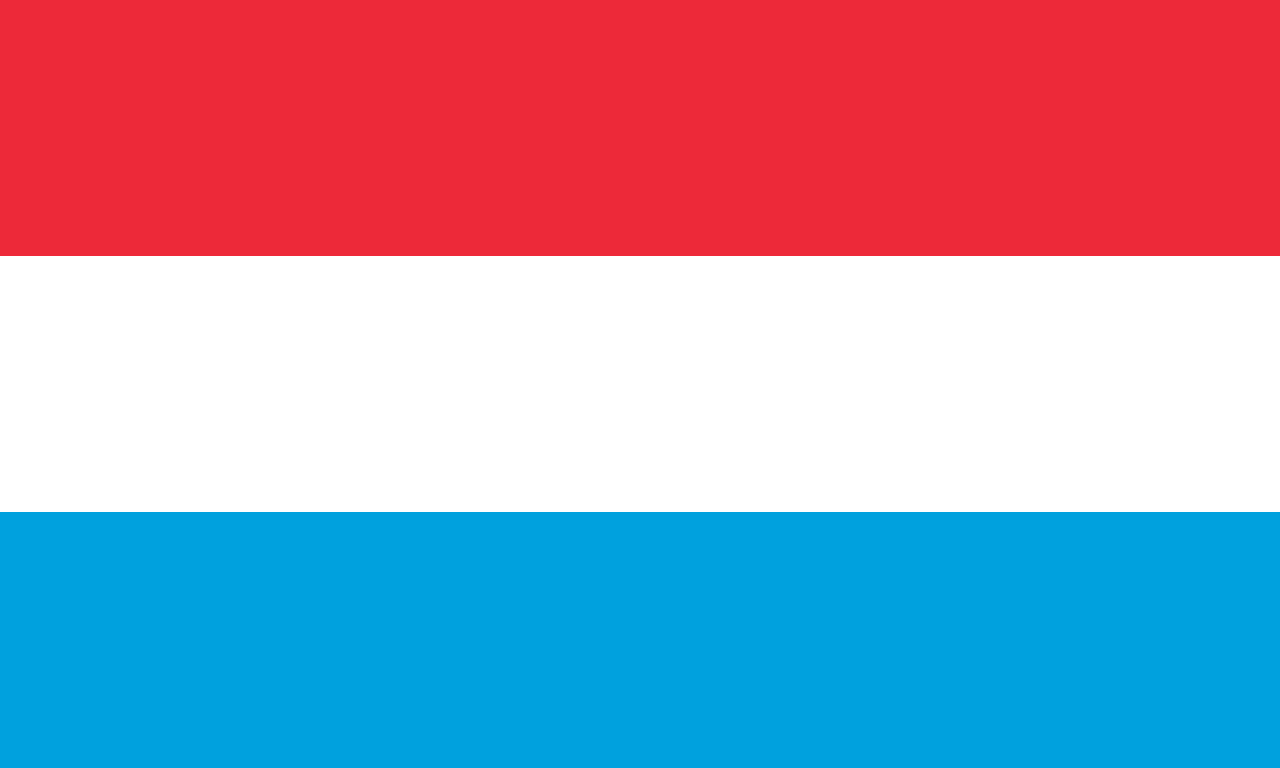

Luxembourg
Europe
Three horizontal stripes of red, white, and light blue representing the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, one of Europe's smallest but wealthiest nations and a founding member of the European Union.