Botswana Flag Meaning
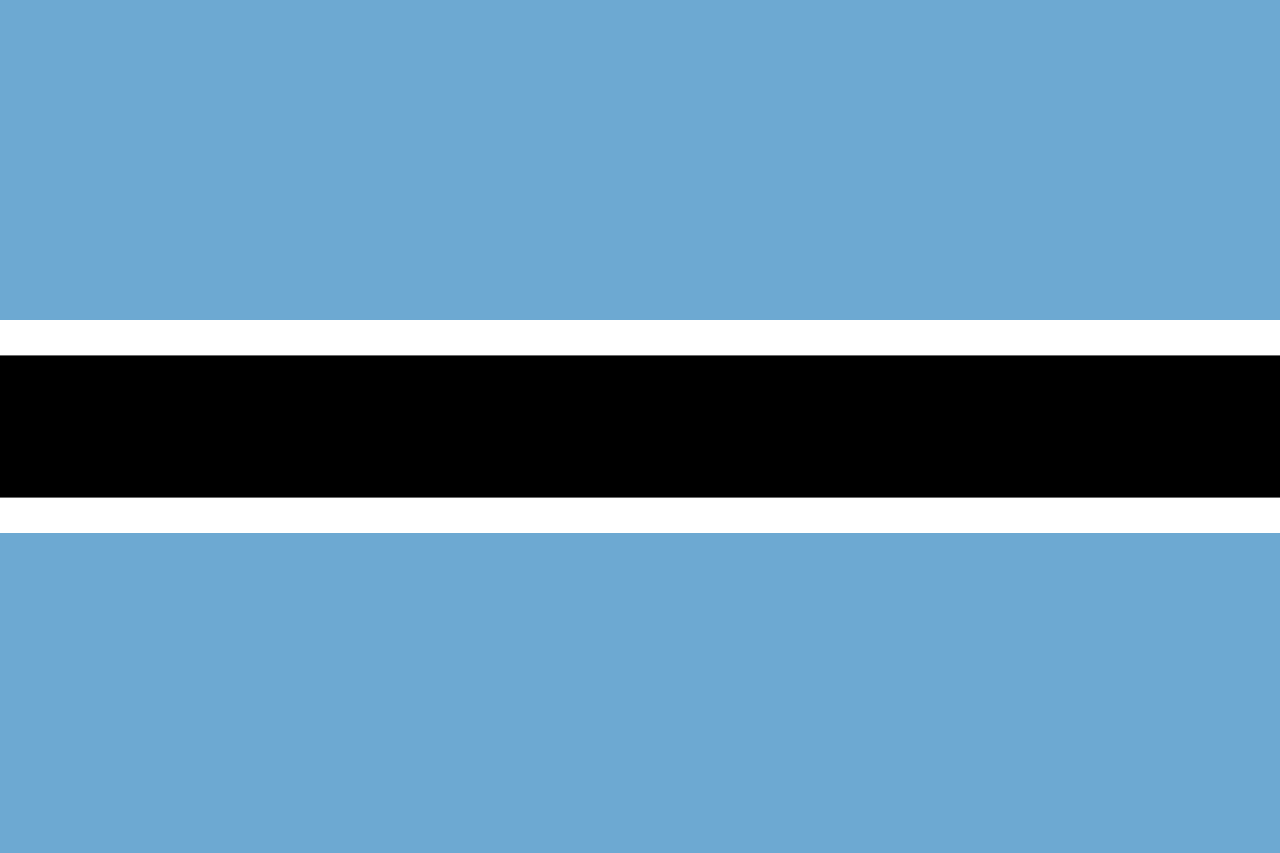
Light blue field with a central black horizontal stripe bordered by thin white stripes, representing the life-giving rains, racial harmony, and the zebra that symbolizes the coexistence of black and white people in peace.
- Continent
- Africa
- Adopted
- 1966
- Ratio
- 2:3
- Colors
- light blue, white, black
- Designer
- Unknown
Symbolism
Light Blue Field: Represents water and the sky, symbolizing the vital importance of rain in this semi-arid country and the hope for prosperity that water brings to the Kalahari Desert region.
Black Stripe: Represents the majority black population of Botswana and the rich cultural heritage of the Tswana people, as well as the unity and strength of the African population.
White Borders: Represent the minority white population and other ethnic groups, symbolizing racial harmony and the peaceful coexistence of all people regardless of race or ethnicity in the diverse society.
Zebra Symbolism: The black and white stripes specifically evoke the zebra, which lives harmoniously in Botswana's wildlife and represents the peaceful coexistence of different races in the rainbow nation.
History
- 1000-1800: Various Tswana chiefdoms established settlements across the region, developing a pastoral economy based on cattle herding and developing sophisticated political systems under traditional chiefs.
- 1820s-1830s: The Mfecane (forced migrations) brought displacement and conflict as Zulu expansion under Shaka pushed other groups northward into Tswana territory, creating political instability.
- 1840s-1880s: European missionaries and traders arrived, with David Livingstone and the London Missionary Society establishing missions while Tswana chiefs like Khama III embraced Christianity and Western education.
- 1885: The Bechuanaland Protectorate was established by Britain at the request of Tswana chiefs seeking protection from Boer expansion and German colonization from South West Africa.
- 1895: Three Tswana chiefs - Khama III, Bathoen I, and Sebele I - traveled to London to successfully petition Queen Victoria to maintain protectorate status rather than transfer to the British South Africa Company.
- 1920s-1950s: Limited colonial development left the protectorate as one of Britain's poorest colonies, with most young men migrating to South African mines for work, creating a labor reserve economy.
- 1960-1965: Political awakening led to the formation of the Bechuanaland Democratic Party under Seretse Khama, who had earlier been exiled for marrying a white British woman but returned to lead independence negotiations.
- September 30, 1966: Botswana gained independence from Britain with Seretse Khama as the first president, adopting the current flag design and establishing a democratic, multi-party system.
- 1967: Diamond deposits were discovered at Orapa, transforming Botswana from one of the world's poorest countries into one of Africa's most prosperous nations within two decades.
- 1980-1998: Under Presidents Khama and his successor Quett Masire, Botswana maintained democratic governance and economic growth, becoming a model for African development and democracy.
- 1990s-2000s: The HIV/AIDS epidemic devastated Botswana, which had one of the world's highest infection rates, but the government implemented comprehensive treatment programs with international support.
- 2008-Present: Democratic transitions have continued with presidents Ian Khama (son of Seretse) and Mokgweetsi Masisi, though recent years have seen concerns about democratic backsliding and authoritarian tendencies.
Trivia
- Botswana is the world's largest producer of diamonds by value, with the diamond industry contributing about 80% of export earnings and funding development programs.
- The flag represents one of Africa's oldest continuous democracies, with peaceful transfers of power since independence in 1966.
- Botswana has transformed from one of the world's poorest countries at independence to an upper-middle-income country, one of Africa's greatest development success stories.
- The Kalahari Desert covers about 80% of the country, making Botswana largely semi-arid despite the blue on its flag representing the vital importance of water.
- Setswana and English are the official languages, with Setswana being spoken by most of the population and serving as a unifying factor across different ethnic groups.
- The Okavango Delta, a UNESCO World Heritage site, is one of the world's largest inland deltas and supports an incredible diversity of wildlife including elephants, lions, and hippos.
- Botswana has the world's largest elephant population, with over 130,000 elephants, though this has created human-wildlife conflict in rural areas.
- The flag flies over a sparsely populated country with only about 2.4 million people in an area larger than France, making it one of the least densely populated countries in the world.
- Cattle traditionally play a central role in Tswana culture, serving not just as economic assets but as symbols of wealth, status, and cultural identity.
- Botswana is completely landlocked and depends on South Africa for most of its trade routes, making regional relationships crucial for economic development.
- The country has made remarkable progress in education, achieving near-universal primary enrollment and high literacy rates within a generation of independence.
- Traditional music and dance remain important, with the Tsutsube dance and setapa (traditional poetry) playing central roles in cultural celebrations.
- Botswana's pula currency is named after the Setswana word for rain, reflecting the vital importance of water in this semi-arid environment.
- The flag represents a country that has successfully managed its diamond wealth through the Debswana partnership with De Beers, avoiding the 'resource curse' that affects many African nations.
- Despite economic success, Botswana faces challenges with income inequality, unemployment, and economic diversification beyond diamonds and cattle.
Related Countries

Zimbabwe
Africa
Seven horizontal stripes alternating green, yellow, red, black, red, yellow, green with a white triangle at the hoist containing a red five-pointed star and the Zimbabwe Bird, representing the nation's agricultural wealth, mineral resources, blood shed for independence, the African people, peace, and the ancient civilization of Great Zimbabwe.
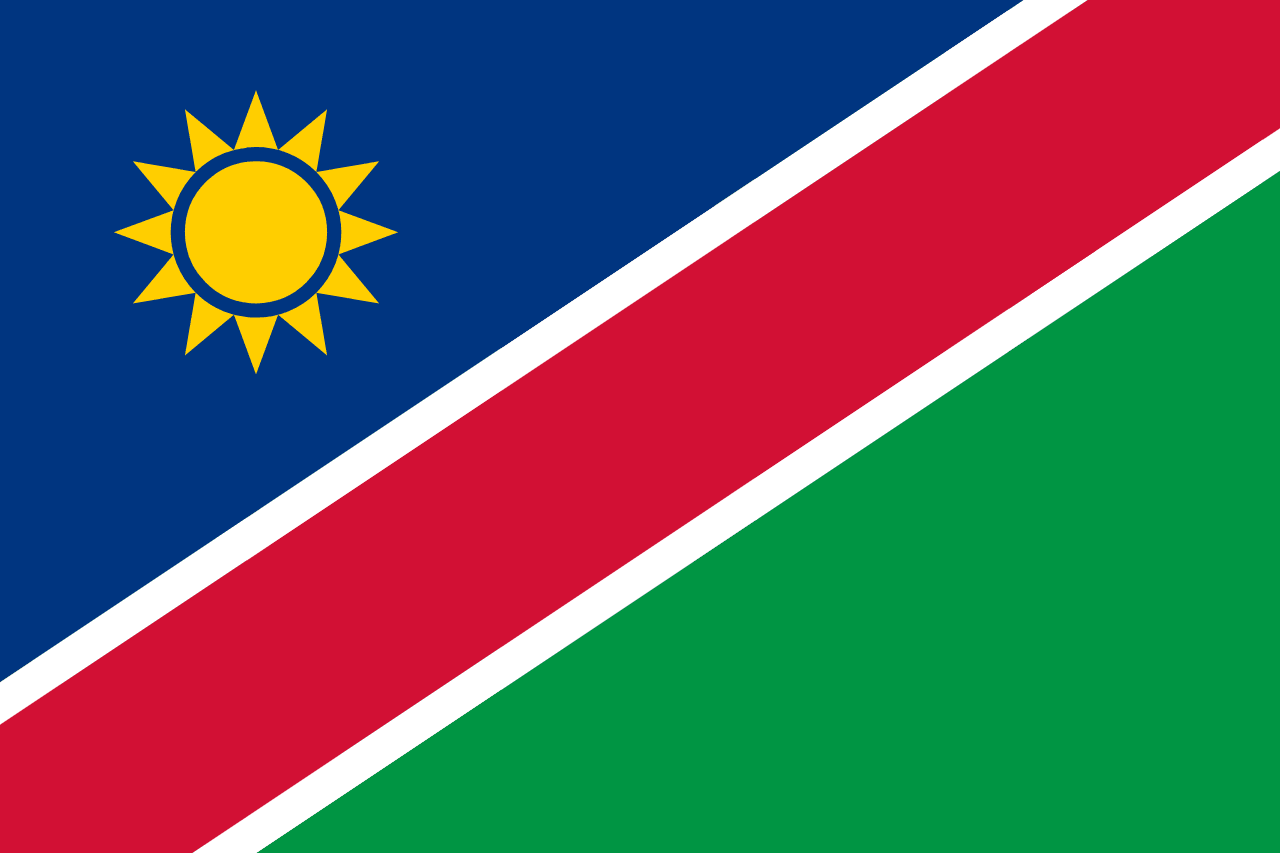
namibia
Africa
A diagonal tricolor divided from the lower hoist to upper fly by a red band with white borders, with blue in the upper hoist containing a golden sun, and green in the lower fly. The design symbolizes Namibia’s land, people, and resources.
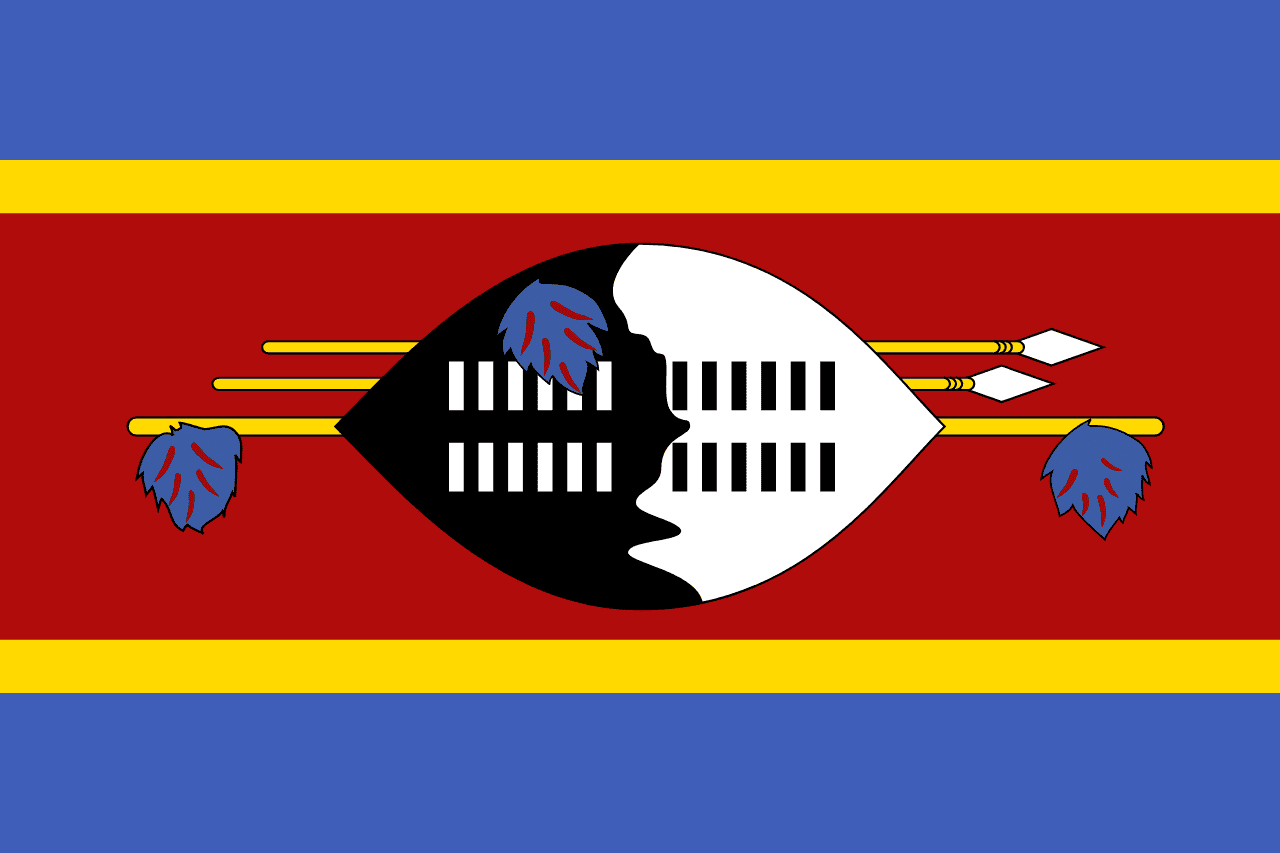
Eswatini
Africa
Five horizontal stripes of blue, yellow, red, yellow, and blue with a traditional Swazi shield and two spears overlaid on the center red stripe, representing peace, mineral wealth, past struggles, and the protection of the kingdom.
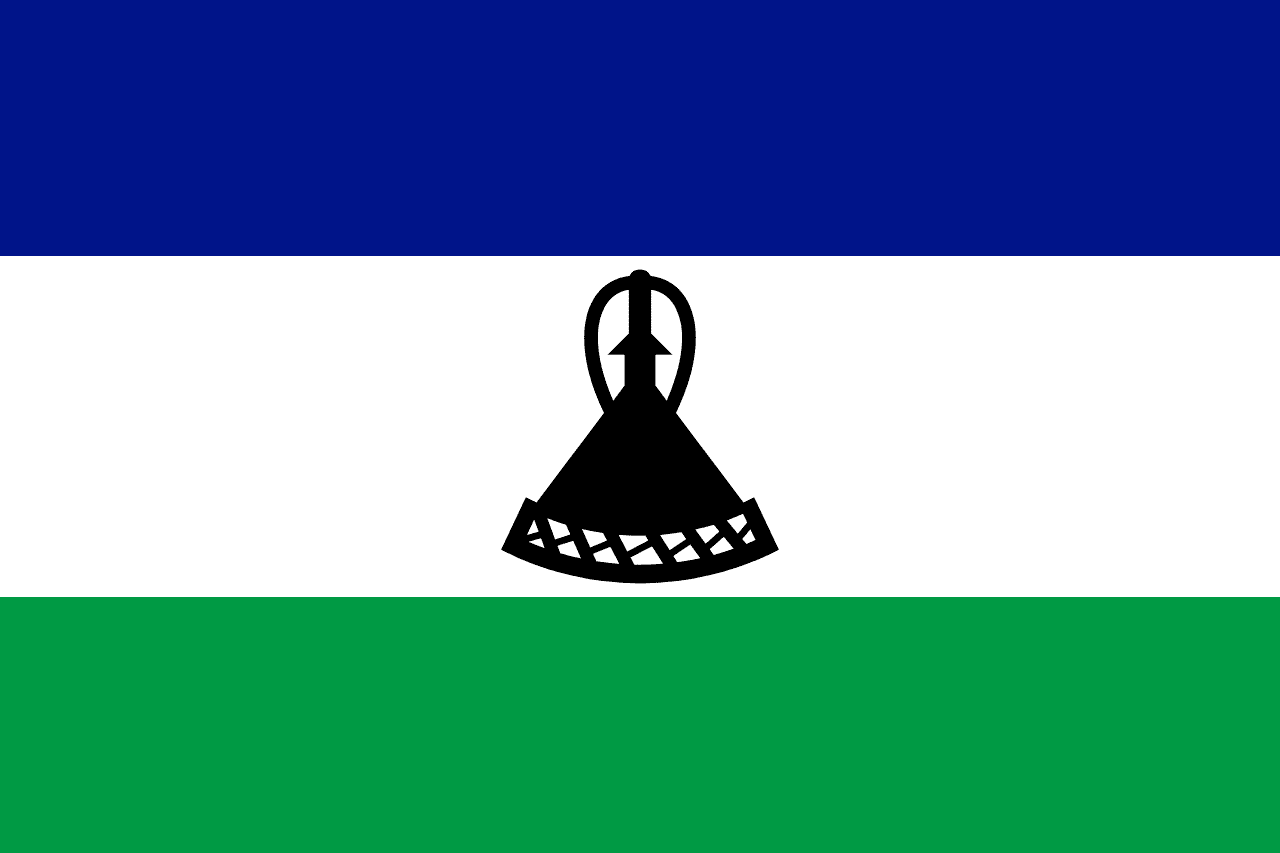

Lesotho
Africa
Three horizontal stripes of blue, white, and green with a black traditional Basotho hat (mokorotlo) centered on the white stripe, representing peace, rain, prosperity, and the cultural heritage of this mountain kingdom completely surrounded by South Africa.
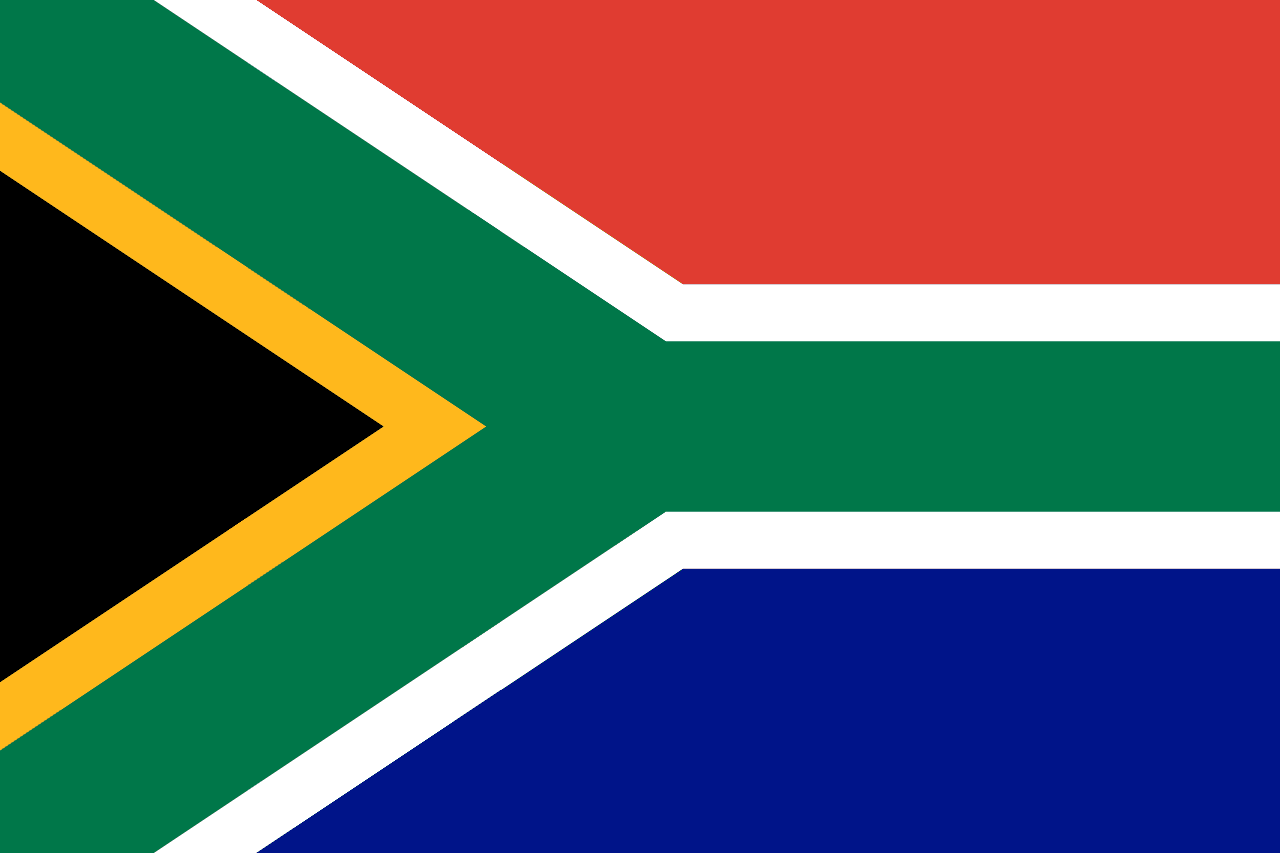

South Africa
Africa
A Y-shaped design with six colors converging toward the flag pole, representing the convergence of diverse elements in South African society and the country's path forward as a unified nation after the end of apartheid and the transition to democracy.
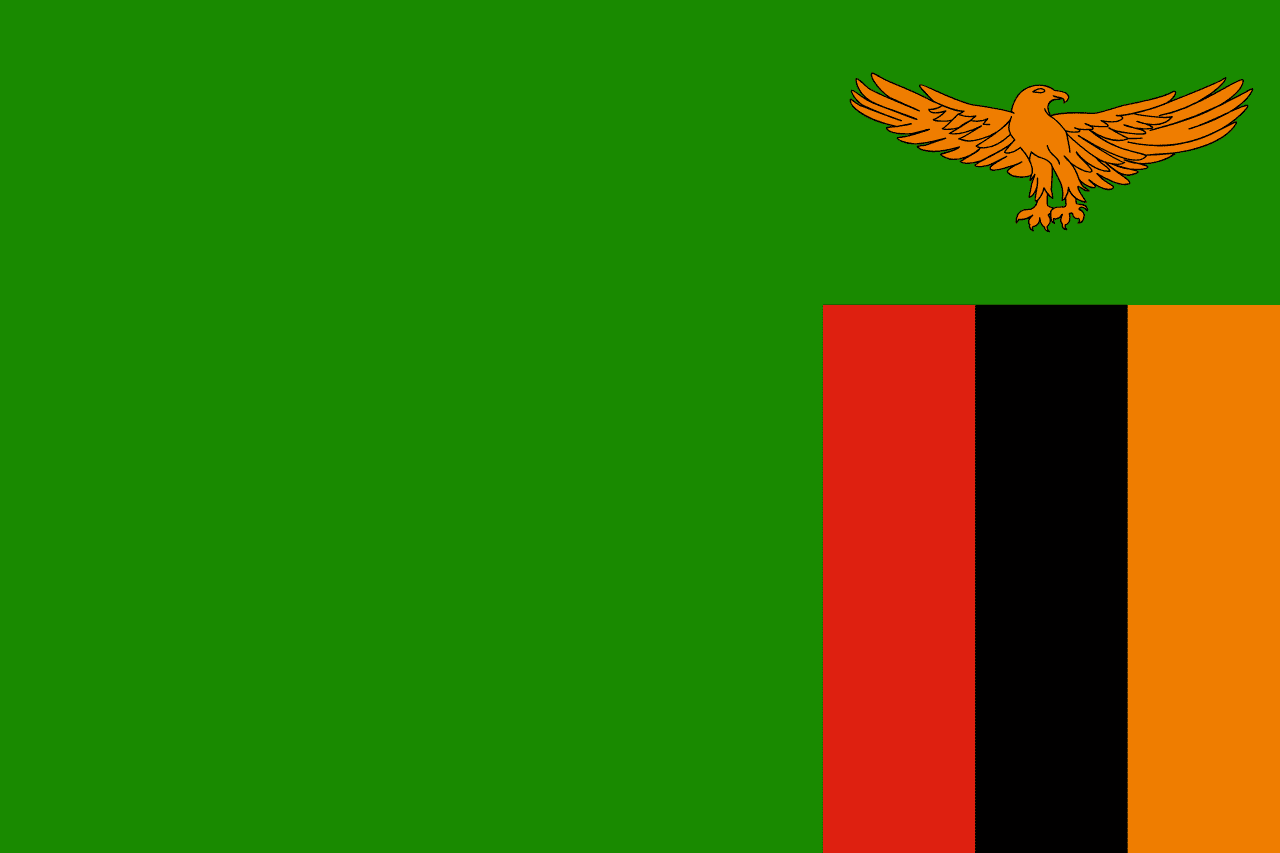
Zambia
Africa
A green field with three vertical stripes of red, black, and orange in the lower right corner and an orange eagle above the stripes, representing the country's natural wealth, the struggle for freedom, the African heritage, the mineral wealth (particularly copper), and the ability to rise above problems.