Bosnia and Herzegovina Flag Meaning
A blue field with a yellow triangle along the hoist and a line of white stars along the triangle's hypotenuse, designed to be ethnically neutral and represent the country's European aspirations while avoiding symbols associated with any particular ethnic group.
- Continent
- Europe
- Adopted
- 1998
- Ratio
- 1:2
- Colors
- blue, yellow, white
- Designer
- Westendorp Commission

Symbolism
Blue Field: Represents Europe and Bosnia's aspiration for European integration, chosen as a neutral color that does not favor any of the three main ethnic groups (Bosniaks, Serbs, and Croats) in the country.
Yellow Triangle: Represents the approximate geographical shape of Bosnia and Herzegovina and symbolizes equality among the three constituent peoples, with its three sides representing the three main ethnic groups.
White Stars: Originally intended to continue infinitely to represent hope and the boundless aspirations of the people, with the visible stars symbolizing Europe and the desire for Euro-Atlantic integration.
Overall Design: Deliberately avoids traditional Bosnian, Serbian, or Croatian symbols to serve as a neutral flag for all citizens regardless of ethnicity, religion, or cultural background in the multi-ethnic state.
History
- Medieval Period: The medieval Bosnian Kingdom flourished under rulers like Ban Kulin and King Tvrtko I, developing a unique identity that blended Catholic, Orthodox, and Bogomil religious influences.
- 1463-1878: Ottoman conquest brought Islam to Bosnia, creating a unique multi-religious society where many Slavs converted to Islam, becoming known as Bosniaks, while others remained Christian.
- 1878-1918: Austro-Hungarian administration modernized Bosnia with railways, schools, and industry while maintaining religious diversity, but also fostering competing national consciousness among Slavic peoples.
- June 28, 1914: Archduke Franz Ferdinand was assassinated in Sarajevo by Gavrilo Princip, a Bosnian Serb nationalist, triggering World War I and the collapse of Austria-Hungary.
- 1918-1941: Bosnia became part of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia under Serbian dominance, with growing tensions between centralist Serbian policies and autonomist Croatian and Bosnian aspirations.
- 1941-1945: World War II brought horrific ethnic violence as the Nazi-allied Ustasha regime in Croatia persecuted Serbs, Jews, and Roma, while communist Partisans fought for a multi-ethnic Yugoslavia.
- 1945-1980: Socialist Yugoslavia under Josip Broz Tito established Bosnia and Herzegovina as one of six republics, promoting 'Brotherhood and Unity' while suppressing ethnic nationalism.
- 1980-1990: After Tito's death, economic crisis and rising nationalism led to the breakdown of Yugoslavia as republican leaders increasingly appealed to ethnic constituencies.
- March 3, 1992: Bosnia declared independence following a referendum boycotted by most Serbs, leading to immediate armed conflict as Bosnian Serb forces, backed by Serbia, sought to create ethnically pure territories.
- 1992-1995: The Bosnian War resulted in approximately 100,000 deaths and 2 million refugees, with widespread ethnic cleansing, mass rape, and genocide, particularly the 1995 Srebrenica massacre.
- December 14, 1995: The Dayton Peace Agreement ended the war, creating a complex federal structure with two main entities: the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Republika Srpska.
- February 4, 1998: The current flag was imposed by the High Representative after political leaders failed to agree on a design, creating a neutral symbol to replace the controversial lily flag.
- 2003-Present: Bosnia has struggled with political dysfunction due to its complex constitutional structure, while pursuing EU membership and dealing with war crimes prosecution and reconciliation efforts.
Trivia
- Bosnia and Herzegovina has one of the most complex government structures in the world, with a rotating three-member presidency representing each major ethnic group.
- The flag was designed by foreigners because local politicians could not agree on a design, making it one of the few national flags created by international intervention.
- Sarajevo hosted the 1984 Winter Olympics and was known as a cosmopolitan, multi-ethnic city before the 1992-1996 siege, one of the longest in modern warfare history.
- The country is roughly triangular in shape, which the yellow triangle on the flag represents, with a small coastline of only 20 kilometers along the Adriatic Sea.
- Bosnian, Croatian, and Serbian are all official languages, though they are essentially the same language with different scripts and some vocabulary differences.
- The flag represents a country where about 50% are Bosniaks (Muslims), 31% are Serbs (Orthodox), and 15% are Croats (Catholic), making it one of Europe's most religiously diverse nations.
- Mostar's Old Bridge, destroyed during the war and rebuilt, is a UNESCO World Heritage site symbolizing reconciliation and the country's Ottoman architectural heritage.
- Bosnia has a rich coffee culture inherited from the Ottoman period, with traditional Bosnian coffee preparation being an important social ritual.
- The country sits at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, creating a unique blend of Ottoman, Austro-Hungarian, and Yugoslav influences in its culture.
- Traditional music includes sevdalinka, melancholic folk songs that reflect the complex history and multicultural heritage of the region.
- Bosnia and Herzegovina is known for its natural beauty, including the Dinaric Alps, pristine rivers like the Neretva and Una, and medieval towns like Jajce and Počitelj.
- The flag flies over a country still dealing with war legacy issues, including war crimes trials, missing persons, and the challenge of building a shared national identity.
- Ćevapi, small grilled meat sausages served with bread and onions, is considered the national dish and reflects the Turkish culinary influence on Bosnian cuisine.
- The country has struggled economically since the war, with high unemployment and emigration, particularly among young people seeking opportunities abroad.
- Despite political challenges, Bosnia has a vibrant civil society and cultural scene, with Sarajevo remaining an important cultural center in the Balkans.
Related Countries
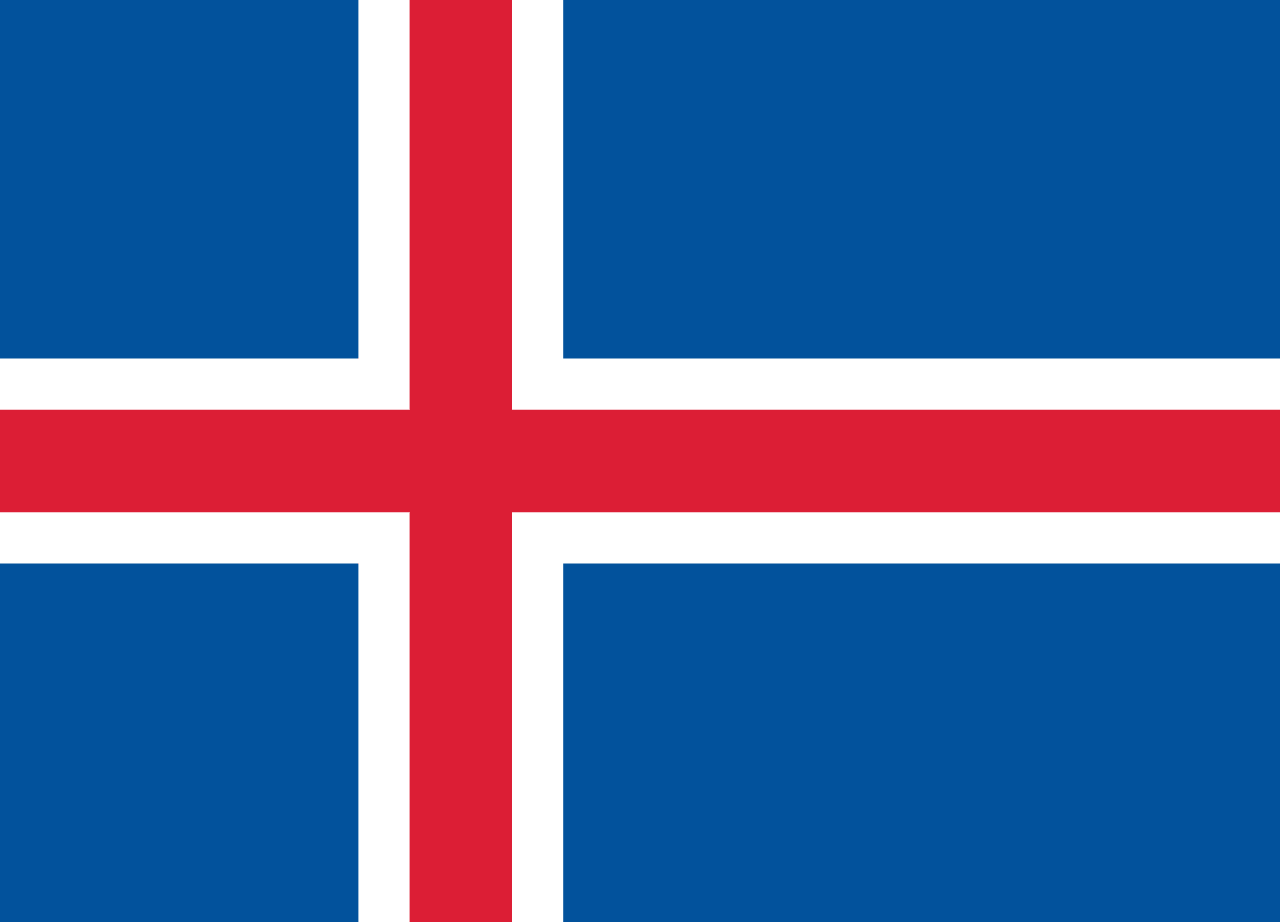
Iceland
Europe
A blue field with a white-bordered red Nordic cross slightly offset toward the hoist, representing Iceland's Nordic heritage, Christian history, and the natural elements of fire and ice that define the island nation.

Montenegro
Europe
A red field with golden border and the coat of arms featuring a golden double-headed eagle, representing Montenegro's medieval heritage, Orthodox Christian identity, and recent independence from Serbia.
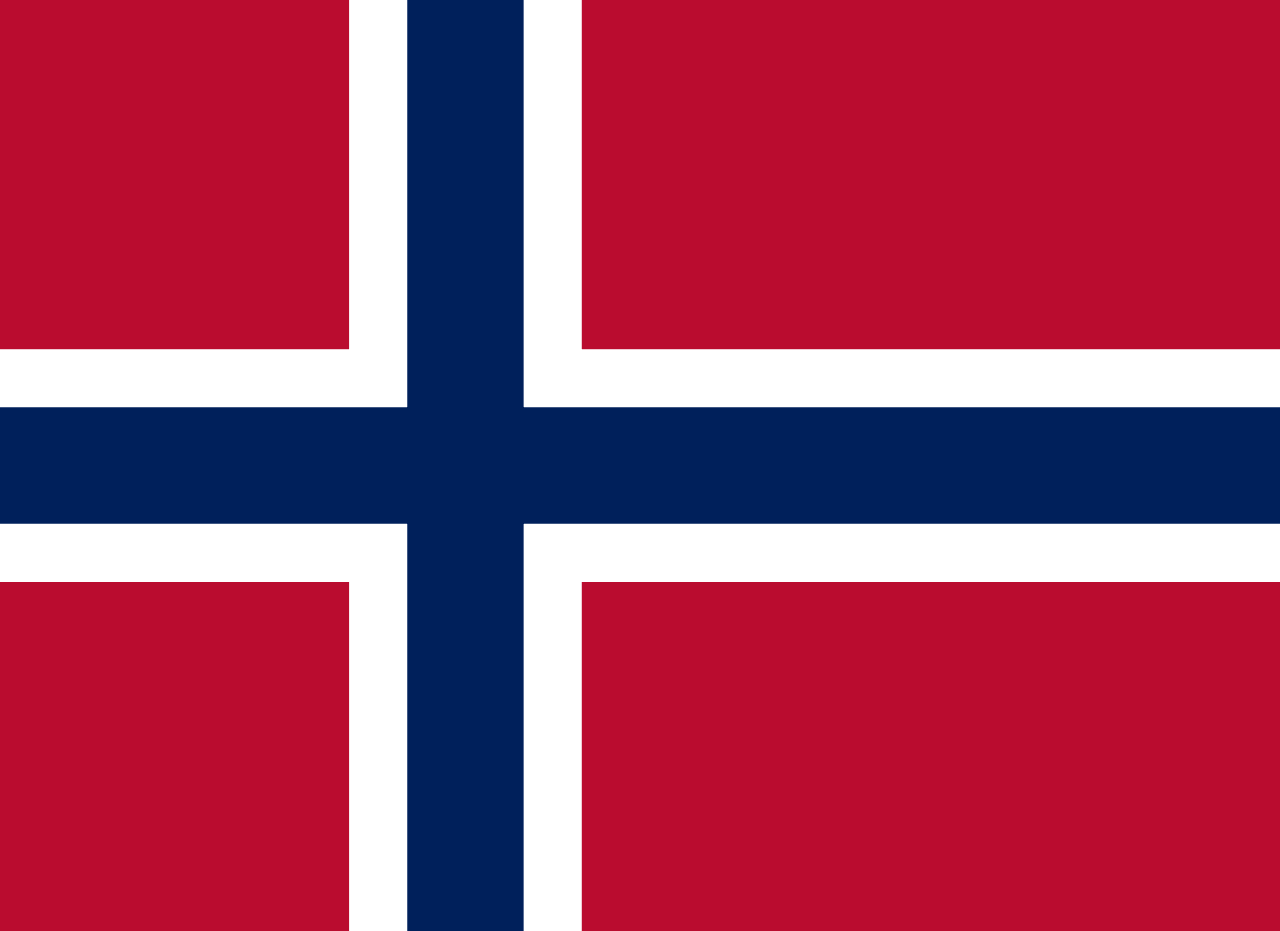
Norway
Europe
Nordic cross design with red field, white cross, and blue outline, symbolizing Norwegian independence and Scandinavian heritage.
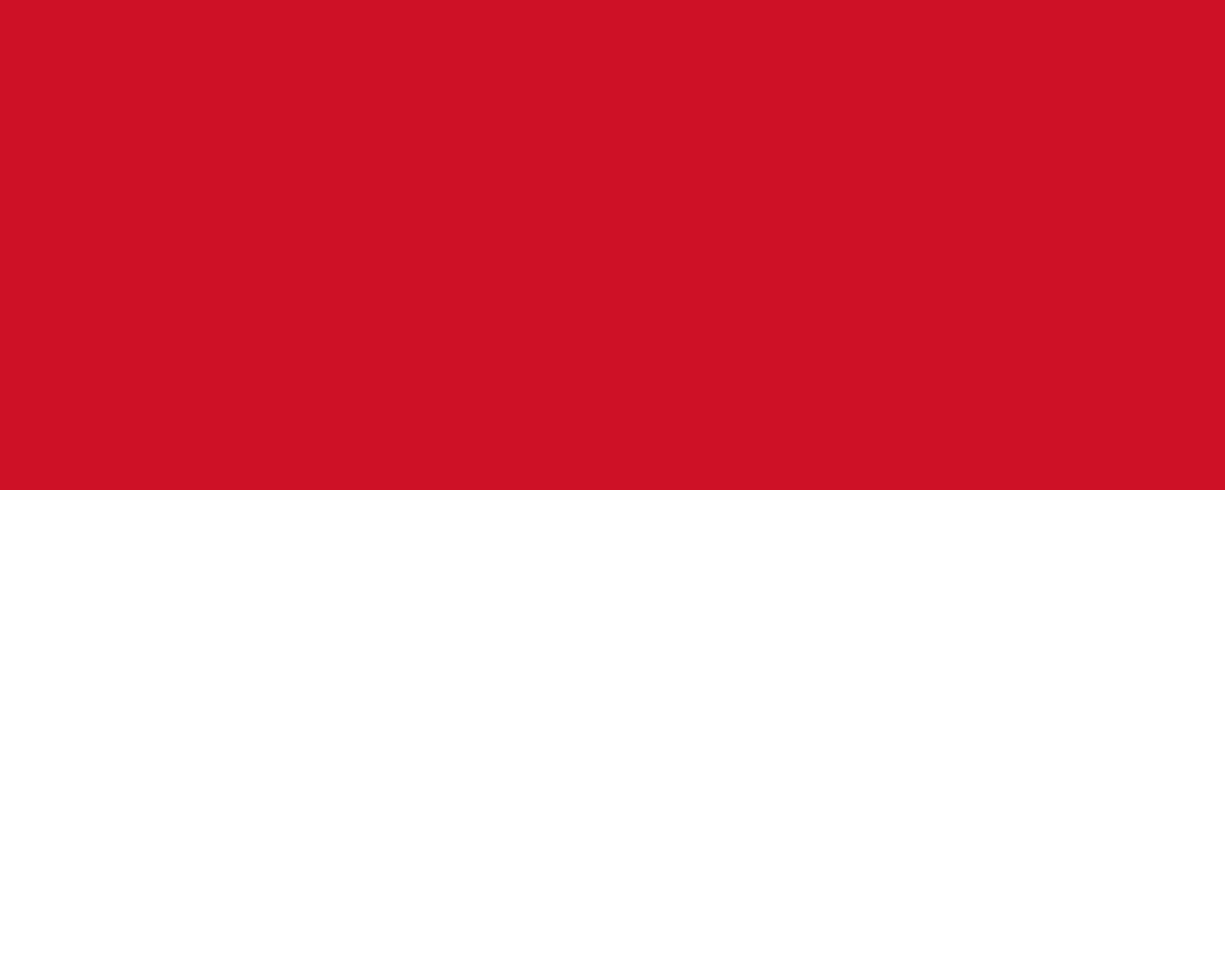

Monaco
Europe
Two horizontal stripes of red and white derived from the heraldic colors of the House of Grimaldi, representing one of the world's smallest sovereign states and oldest ruling dynasties.
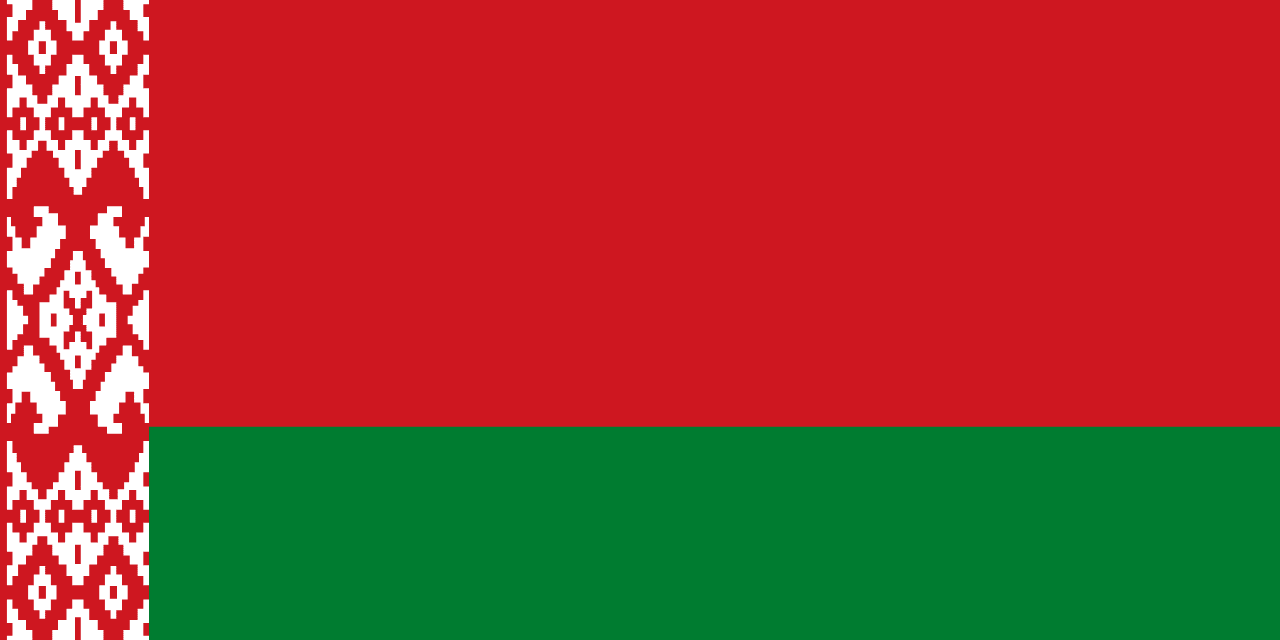

Belarus
Europe
A red horizontal stripe over a green stripe with a traditional red and white ornamental pattern on the hoist side, representing the historical heritage of Belarus, its forests and agriculture, and the decorative folk art traditions that define Belarusian cultural identity.

Switzerland
Europe
A red square field with a white Greek cross in the center, representing the Christian faith that united the early Swiss cantons and the blood shed in defense of freedom, with origins dating back to the Holy Roman Empire and medieval Swiss military banners.